28 start with D start with D

William Henry Harrison Clayton was one of nearly 75,000 soldiers from Iowa to join the Union ranks during the Civil War. Possessing a high school education and superior penmanship, Clayton served as a company clerk in the 19th Infantry, witnessing battles in the Trans-Mississippi theater. His diary and his correspondence with his family in Van Buren County form a unique narrative of the day-to-day soldier life as well as an eyewitness account of critical battles and a prisoner-of-war camp.
Clayton participated in the siege of Vicksburg and took part in operations against Mobile, but his writings are unique for the descriptions he gives of lesser-known but pivotal battles of the Civil War in the West. Fighting in the Battle of Prairie Grove, the 19th Infantry sustained the highest casualties of any federal regiment on the field. Clayton survived that battle with only minor injuries, but he was later captured at the Battle of Stirling's Plantation and served a period of ten months in captivity at Camp Ford, Texas.
Clayton's writing reveals the complicated sympathies and prejudices prevalent among Union soldiers and civilians of that period in the country's history. He observes with great sadness the brutal effects of war on the South, sympathizing with the plight of refugees and lamenting the destruction of property. He excoriates draft evaders and Copperheads back home, conveying the intra-sectional acrimony wrought by civil war. Finally, his racist views toward blacks demonstrate a common but ironic attitude among Union soldiers whose efforts helped lead to the abolition of slavery in the United States.

Daughters of the Union casts a spotlight on some of the most overlooked and least understood participants in the American Civil War: the women of the North. Unlike their Confederate counterparts, who were often caught in the midst of the conflict, most Northern women remained far from the dangers of battle. Nonetheless, they enlisted in the Union cause on their home ground, and the experience transformed their lives.
Nina Silber traces the emergence of a new sense of self and citizenship among the women left behind by Union soldiers. She offers a complex account, bolstered by women's own words from diaries and letters, of the changes in activity and attitude wrought by the war. Women became wage-earners, participants in partisan politics, and active contributors to the war effort. But even as their political and civic identities expanded, they were expected to subordinate themselves to male-dominated government and military bureaucracies.
Silber's arresting tale fills an important gap in women's history. She shows the women of the North--many for the first time--discovering their patriotism as well as their ability to confront new economic and political challenges, even as they encountered the obstacles of wartime rule. The Civil War required many women to act with greater independence in running their households and in expressing their political views. It brought women more firmly into the civic sphere and ultimately gave them new public roles, which would prove crucial starting points for the late-nineteenth-century feminist struggle for social and political equality.

A mid-level Confederate official and lawyer in secessionist North Carolina, David Schenck (1835–1902) penned extensive diaries that have long been a wellspring of information for historians. In the midst of the secession crisis, Schenck overcame long-established social barriers and reshaped antebellum notions of manhood, religion, and respectability into the image of a Confederate nationalist. He helped found the revolutionary States’ Rights Party and relentlessly pursued his vision of an idealized Southern society even after the collapse of the Confederacy. In the first biography of this complicated figure, Rodney Steward opens a window into the heart and soul of the Confederate South’s burgeoning professional middle class and reveals the complex set of desires, aspirations, and motivations that inspired men like Schenck to cast for themselves a Confederate identity that would endure the trials of war, the hardship of Reconstruction, and the birth of a New South.
After secession, Schenck remained on the home front as a receiver under the Act of Sequestration, enriching himself on the confiscated property of those he accused of disloyalty. After the war, his position as a leader in the Ku Klux Klan and his resistance to Radical Reconstruction policies won him a seat on the superior court bench, but scathing newspaper articles about his past upended a bid for chief justice of the North Carolina Supreme Court, a compelling fall from grace that reveals much about the shifting currents in North Carolina society and politics in the years after Reconstruction. During the last twenty years of his life, spent in Greensboro, Schenck created the Guilford Battleground Company in an effort to redeem the honor of the Tar Heels who fought there and his own honor as well.
Schenck’s life story provides a powerful new lens to examine and challenge widely held interpretations of secessionists, Confederate identity, Civil War economics, and home-front policies. Far more than a standard biography, this compelling volume challenges the historiography of the Confederacy at many levels and offers a sophisticated analysis of the evolution of a Confederate identity over a half century.
Rodney Steward is an assistant professor of history at the University of South Carolina, Salkehatchie. His works have appeared in the Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Encyclopedia of North Carolina, and North Carolina Historical Review.



In the fall of 1862, after a leadership shake-up initiated by Lincoln, Gen. Ambrose Burnside assumed command of the Army of the Potomac and developed an aggressive plan to attack the Confederate capital of Richmond. However, in order to reach Richmond, Burnside had to march through Fredericksburg, where Gen. Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia was well entrenched. After crossing the Rappahannock River under enemy fire, Burnside and his troops engaged Lee’s army within the city, then launched a futile frontal assault against a heavily fortified ridge west of Fredericksburg. The end result was a decisive victory for the Confederacy, as the Union army suffered more than double the number of casualties as its foes. Burnside would resign a month later but would resurface as war in the Western Theater grew heated.
Decisions at Fredericksburg explores the critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders during the battle and how these decisions shaped its outcome. Rather than offering a history of the battle, Chris Mackowski hones in on a sequence of critical decisions made by commanders on both sides of the contest to provide a blueprint of the Battle of Fredericksburg at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of the battle to progress from knowledge of what happened to a mature grasp of why events happened.
Complete with maps and a driving tour, Decisions at Fredericksburg is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a concise introduction to the battle can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions at Fredericksburg is the eleventh in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.

Decisions at Kennesaw Mountain explores the critical decisions made by Confederate and Federal commanders during the battle and how these decisions shaped its outcome. Rather than offering a history of the battle, Larry Peterson hones in on a sequence of command decisions that provides us, retroactively, with a blueprint of the Battle of Kennesaw Mountain at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of the battle to progress from a knowledge of what happened to a mature grasp of why events happened.
Complete with maps and a driving tour, Decisions at Kennesaw Mountain is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a concise introduction to the battle can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions at Kennesaw Mountain is the seventeenth in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.

The largest battle fought in Kentucky during the American Civil War occurred at a small, crossroads town named Perryville. As Gen. Braxton Bragg’s Confederate Heartland Offensive sputtered through Kentucky, Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell’s reformed Army of the Ohio pursued the Army of the Mississippi and clashed with its rearguard just outside Perryville. Believing that he faced only a part of Buell’s army, Bragg ordered an assault on the Union left flank which resulted in Confederate victory. However, that evening Bragg determined the Army of the Ohio outnumbered him three to one and quickly decided to retreat. Outmanned, outmaneuvered, and lacking supplies and reinforcements, Bragg retreated through the Cumberland Gap into East Tennessee, and Kentucky remained in Union control for the rest of the Civil War.
Decisions at Perryville explores the critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders during the battle and how these decisions shaped its outcome. Rather than offering a history of the battle, Larry Peterson hones in on a sequence of critical decisions made by commanders on both sides of the contest to provide a blueprint of the Battle of Perryville at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of the battle to progress from a knowledge of what happened to a mature grasp of why events happened.
Complete with maps and a driving tour, Decisions at Perryville is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a concise introduction to the battle can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions at Perryville is the eleventh in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.

The successive battles of The Wilderness and Spotsylvania Court House opened Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant’s 1864 Overland Campaign. As the first confrontation between Union and Confederate leaders Grant and Gen. Robert E. Lee, these two bloody battles signaled the new reality of war. The fighting at the Battle of The Wilderness, immediately followed by the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, was costly for both sides, and while the Union army could replace its losses, Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia could not. It would be exactly one year from Grant’s orders to Gen. George G. Meade stating that Lee’s army would be his objective until the surrender at Appomattox.
Decisions at The Wilderness and Spotsylvania Court House introduces readers to critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders throughout the two costly meetings. Dave Townsend examines the decisions that prefigured the action and shaped the course of each battle as it unfolded. Rather than a linear history of the battles, Townsend’s discussion of the critical decisions presents readers with a vivid blueprint of the battles’ developments. Exploring the critical decisions in this way allows the reader to progress from a sense of what happened in these battles to why they happened as they did.
Complete with maps and a guided tour, Decisions at The Wilderness and Spotsylvania Court House is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for concise introductions to the battles can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the battles and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions at The Wilderness and Spotsylvania Court House is the seventh in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.

Decisions of the 1862 Kentucky Campaign introduces readers to critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders throughout the heartland contest. Rather than offering a history of the Kentucky Campaign, Larry Peterson hones in on a sequence of critical decisions confronting commanders on both sides of the clash to provide a blueprint of the campaign at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of history to go from a rudimentary sense of the what of warfare, to a mature grasp of why.
Complete with maps and a guided tour, Decisions of the 1862 Kentucky Campaign is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a digestible introduction to the campaign’s battles can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions of the 1862 Kentucky Campaign is the sixth in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.
LARRY PETERSON retired from United Airlines as a Boeing 757/767 Standard Captain. He is the author of Confederate Combat Commander: The Remarkable Life of Brigadier General Alfred Jefferson Vaughn Jr. and Decisions at Chattanooga.

Decisions of the 1862 Shenandoah Valley Campaign explores the critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders during the battle and how these decisions shaped its outcome. Rather than offering a history of the battle, Robert G. Tanner hones in on a sequence of critical decisions made by commanders on both sides of the contest to provide a blueprint of Jackson’s Valley Campaign at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of the battle to progress from a knowledge of what happened to a mature grasp of why events happened.
Complete with maps and a driving tour, Decisions of the 1862 Shenandoah Valley Campaign is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a concise introduction to the battle can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions of the 1862 Shenandoah Valley Campaign is the seventeenth in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.

From June 25 to July 1, 1862, Gen. Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia engaged Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan’s Army of the Potomac in a series of battles at the end of the Peninsula Campaign that would collectively become known as the Seven Days Battles. Beginning with the fighting at the Battle of Beaver Dam Creek, Lee consistently maneuvered against and attacked McClellan’s Army of the Potomac as it retreated south across the Virginia Peninsula to the James River. At the conclusion of the Battle of Malvern Hill, Lee’s second most costly battle, where McClellan’s strong defensive position of infantry and artillery repelled multiple frontal assaults by Lee’s troops, the Federal army slipped from Lee’s grasp and brought the Seven Days to an end. The Seven Days was a clear Confederate victory that drove the Union army away from the capital at Richmond, began the ascendancy of Robert E. Lee, and commenced a change in the war in the Eastern Theater. It set the stage for the Second Manassas Campaign followed by the Maryland Campaign of 1862.
Decisions of the Seven Days explores the critical decisions made by Confederate and Union commanders during the Seven Days Battles and how these decisions shaped the outcome. Rather than offering a history of the battles, Matt Spruill hones in on a sequence of critical decisions made by commanders on both sides of the contests to provide a blueprint of the Seven Days at its tactical core. Identifying and exploring the critical decisions in this way allows students of the battles to progress from knowledge of what happened to a mature grasp of why events happened.
Complete with maps and a driving tour, Decisions of the Seven Days is an indispensable primer, and readers looking for a concise introduction to the battles can tour this sacred ground—or read about it at their leisure—with key insights into the campaign and a deeper understanding of the Civil War itself.
Decisions of the Seven Days is the tenth in a series of books that will explore the critical decisions of major campaigns and battles of the Civil War.


The first book-length study of one of the Civil War's most outlandish and mysterious characters
Devil's Game traces the amazing career of Charles A. Dunham, Civil War spy, forger, journalist, and master of dirty tricks. Writing for a variety of New York papers under alternate names, Dunham routinely faked stories, created new identities, and later boldly cast himself to play those roles. He achieved his greatest infamy when he was called to testify in Washington concerning Abraham Lincoln's assassination. Many parts of Dunham's career remain shadowy, but Cumming offers the first detailed tour of Dunham's convoluted, high-stakes, international deceits, including his effort to sell Lincoln on plans for a raid to capture Jefferson Davis.
Exhaustively researched and unprecedented in depth, this carefully crafted assessment of Dunham's motives, personality, and the complex effects of his schemes changes assumptions about covert operations during the Civil War.


In 1854 Caroline Seabury of Brooklyn, New York, set out for Columbus, Mississippi, to teach French at its Institute for Young Ladies. She lived in Columbus until 1863, through the years of mounting sectional bitterness that preceded the Civil War and through the turmoil and hardships of the war itself. During that time, her most intimate confidant was her diary. Discovered in the archives of the Minnesota State Historical Society, it is published here for the first time.
The diary is an illuminating account of southern plantation society and the “peculiar institution” of slavery on the eve of its destruction. Seabury also records her uneasy attempts to come to terms with her position as an unmarried, white, Northern woman whose job was to educate wealthy, white, Southern girls in a setting seemingly oblivious to the horrors of slavery. The diary is not simply a chronicle of daily happenings; Seabury concentrates on remarkable events and the memorable feelings and ideas they generate, shaping them into entries that reveal her as an accomplished writer. She frames her narrative with her journey south in 1854 and the hazardous and exhausting return north through battle lines in 1863.
Disapproving of slavery, yet deeply attached to friends and her life in Columbus and also painfully conscious of the fragility of her own economic and social position, Seabury condemned privately in her diary the evils that she endured silently in public. There are striking scenes of plantation life that depict the brutalities of slavery and benumbed responses to them. Seabury also successfully captures the mood of Mississippi as it changed from a fire-eating appetite to fight the Yankees to a grim apprehension of inexorable defeat. Most impressive of all is Seabury’s poignantly honest presentation of herself, caught in the middle.

and family as Nannie, began a diary. The Diary of Nannie Haskins Williams: A Southern
Woman’s Story of Rebellion and Reconstruction, 1863–1890 provides valuable insights into
the conditions in occupied Middle Tennessee. A young, elite Confederate sympathizer,
Nannie was on the cusp of adulthood with the expectation of becoming a mistress in
a slaveholding society. The war ended this prospect, and her life was forever changed.
Though this is the first time the diaries have been published in full, they are well known
among Civil War scholars, and a voice-over from the wartime diary was used repeatedly
in Ken Burns’s famous PBS program The Civil War.
Sixteen-year-old Nannie had to come to terms with Union occupation very early in
the war. Amid school assignments, young friendship, social events, worries about her
marital prospects, and tension with her mother, Nannie’s entries also mixed information
about battles, neighbors wounded in combat, U.S. Colored troops, and lawlessness in the
surrounding countryside. Providing rare detail about daily life in an occupied city, Nannie’s
diary poignantly recounts how she and those around her continued to fight long after
the war was over—not in battles, but to maintain their lives in a war-torn community.
Though numerous women’s Civil War diaries exist, Nannie’s is unique in that she also
recounts her postwar life and the unexpected financial struggles she and her family experienced
in the post-Reconstruction South. Nannie’s diary may record only one woman’s
experience, but she represents a generation of young women born into a society based
on slavery but who faced mature adulthood in an entirely new world of decreasing farm
values, increasing industrialization, and young women entering the workforce. Civil War
scholars and students alike will learn much from this firsthand account of coming-of-age
during the Civil War.
Minoa D. Uffelman is an associate professor of history at Austin Peay State University.
Ellen Kanervo is professor emerita of communications at Austin Peay State University.
Phyllis Smith is retired from the U.S. Army and currently teaches high school science in
Montgomery County, Tennessee. Eleanor Williams is the Montgomery County, Tennessee,
historian.


Combining literary analysis, cultural history, and feminist theory, Disarming the Nation argues that the Civil War functioned in women's writings to connect female bodies with the body politic. Women writers used the idea of "civil war" as a metaphor to represent struggles between and within women—including struggles against the cultural prescriptions of "civility." At the same time, these writers also reimagined the nation itself, foregrounding women in their visions of America at war and in peace. In a substantial afterword, Young shows how contemporary black and white women—including those who crossdress in Civil War reenactments—continue to reshape the meanings of the war in ways startlingly similar to their nineteenth-century counterparts.
Learned, witty, and accessible, Disarming the Nation provides fresh and compelling perspectives on the Civil War, women's writing, and the many unresolved "civil wars" within American culture today.

William McKnight was a member of the Seventh Ohio Volunteer Cavalry from September 1862 until his death in June of 1864. During his time of service, McKnight penned dozens of emotion-filled letters, primarily to his wife, Samaria, revealing the struggles of an entire family both before and during the war.
This collection of more than one hundred letters provides in-depth accounts of several battles in Kentucky and Tennessee, such as the Cumberland Gap and Knoxville campaigns that were pivotal events in the Western Theater. The letters also vividly respond to General John Hunt Morgan’s raid through Ohio and correct claims previously published that McKnight was part of the forces chasing Morgan. By all accounts Morgan did stay for a period of time at McKnight’s home in Langsville during his raid through Ohio, much to McKnight’s horror and humiliation, but McKnight was in Kentucky at the time. Tragically, McKnight was killed in action nearly a year later during an engagement with Morgan’s men near Cynthiana, Kentucky.

The Civil War was a tragic conflict that destroyed many lives, but for those trying to save lives the tragedy was often compounded. Military doctors labored through the smoke of battle where impossible conditions and fear of infection often forced them to resort to amputation, and most operations were performed without painkillers. Thomas Fanning Wood recorded his wartime experiences as a Confederate Army surgeon, and his recollections of those events allow us to hear a distinct voice of the Civil War.
As a young soldier recovering from fever at a Richmond hospital, Wood developed an interest in medicine that was encouraged by a doctor who steered him toward medical training. After only eight months of study he was made an assistant surgeon in the Third North Carolina Regiment. His narrative—drawn from his memoirs, letters from the front, and articles written for his hometown newspaper—presents a poignant and sometimes horrifying picture of what the Civil War physician had to face both under battlefield conditions and in urban hospitals.
Wood himself spent much of his time at the front, and his vivid narrative describes both a doctor’s daily activities and the campaigns he witnessed. He was present at many of the war’s major engagements: he was near Stonewall Jackson when the general fell at Chancellorsville, manned a field dressing station at the foot of Culp’s Hill at Gettysburg, and was one of the few survivors of the Union attack on the "mule shoe" at Spotsylvania when his entire division was wiped out. Wood’s account also lends new insight into Jubal Early’s 1864 campaigns in the Shenandoah Valley and against Washington.
With its observations of medical care and training not found in standard histories of the war—including a description of the examination required to become an assistant surgeon—Doctor to the Front offers a unique human perspective on the Civil War. With their additional descriptions of key figures and events, Wood’s recollections combine historical significance and human interest to show us another side of that terrible conflict.
The Author: Donald B. Koonce is the great-grandson of Thomas Fanning Wood and has served on the Board of Directors of the South Carolina Historical Society and the Historic Greenville Foundation. He is president of the Koonce Group, Inc., an award-winning communications company whose productions include Daybreak at the Cowpens, a documentary for the National Park Service.

of public policy actions, political speeches, and judicial decisions related to the American
Civil War. Collectively, the four volumes in this series give scholars, teachers, and students
easy access to the full texts of the most important, fundamental documents as well as hardto-
find, rarely published primary sources on this critical period in U.S. history.
The first two volumes of the series, Legislative Achievements and Political Arguments,
were released last year. The final installment, Judicial Decisions, is divided into two volumes.
The first volume, spanning the years 1857 to 1866, was released last year. This second
volume of Judicial Decisions covers the years 1867 to 1896. Included here are some of
the classic judicial decisions of this time such as the 1869 decision in Texas v. White and
the first judicial interpretation of the 1868 Fourteenth Amendment, the 1873 Slaughter-
House Cases. Other decisions are well known to specialists but deserve wider readership
and discussion, such as the 1867 state and 1878 federal cases that upheld the separation of
the races in public accommodations (and thus constituted the common law of common
commerce) long before the more notorious 1896 case of Plessy v. Ferguson (also included).
These judicial voices constitute a lasting and often overlooked aspect of the age of Abraham
Lincoln. Mackey’s headnotes and introductory essays situate cases within their historical
context and trace their lasting significance. In contrast to decisions handed down
during the war, these judicial decisions lasted well past their immediate political and legal
moment and deserve continued scholarship and scrutiny.
This document collection presents the raw “stuff” of the Civil War era so that students,
scholars, and interested readers can measure and gauge how that generation met Lincoln’s
challenge to “think anew, and act anew.” A Documentary History of the American Civil
War Era is an essential acquisition for academic and public libraries in addition to being a
valuable resource for courses on the Civil War and Reconstruction, legal history, political
history, and nineteenth-century American history.

The first volume of the series, Legislative Achievements, contains legislation passed in response to the turmoil seizing the country on the brink of, during, and in the wake of the Civil War. Forthcoming are volume 2, Political Arguments, which contains voices of politicians, political party platforms, and administrative speeches, and volume 3, Judicial Decisions, which provides judicial opinions and decisions as the Civil War raged in the courtrooms as well as on the battlefields.
Organized chronologically, each of the selections is preceded by an introductory headnote that explains the document’s historical significance and traces its lasting impact. These headnotes provide insight into not only law and public policy but also the broad sweep of issues that engaged Civil War–era America.
Legislative Achievements features some of the most momentous and enduring public policy documents from the time, beginning with the controversial September 15, 1850, Fugitive Slave Act and concluding with the June 18, 1878, Posse Comitatus Act. Both military and nonmilitary legislation constitute this part, including the April 19, 1861, proclamation by President Abraham Lincoln declaring a naval blockade on Southern ports and Confederate President Jefferson Davis’s proclamation authorizing blockade runners to attack Northern shipping, both issued on the same day. Nonmilitary legislation includes statutes affecting the postwar period, such as the 1862 Homestead Act, the Civil Rights Act of 1866, and all four of the Reconstruction Acts. Also in this section are the three constitutional amendments, the Habeas Corpus Acts of 1863 and 1867, the Freedman’s Bureau Acts of 1865 and 1866, and the 1867 Tenure of Office Act together with President Andrew Johnson’s message vetoing the Act.
A Documentary History of the American Civil War Era is an essential acquisition for academic and public libraries in addition to being a valuable resource for students of the Civil War and Reconstruction, legal history, public policy, and nineteenth-century American history.
THOMAS C. MACKEY is a professor of history at the University of Louisville and adjunct Professor of Law at Brandeis School of Law. He is the author of Pornography on Trial (2002) and Pursuing Johns (2005).

Volume 2 in the series, Political Arguments, presents the words of politicians, political party platforms, and administrative speeches. It is divided into two sections. The first, Voices of the Politicians and Political Parties, comprises the platforms of the major (and some minor) parties from1856 to 1876. Also included are such pieces as Robert E. Lee’s letter of resignation from the U.S. Army, a few key speeches by that rising politician from Illinois, Abraham Lincoln, and a letter on the “American Question” written by a European observer, Karl Marx. Other items include examples of the 1860–1861 state ordinances of secession and addresses on emancipation and Reconstruction by Jefferson Davis and by the Republican leader in the House of Representatives, Thaddeus Stevens.
Section two, Voices of the Administrations, contains records from the presidencies of James Buchanan, Abraham Lincoln, Andrew Johnson, Ulysses S. Grant, and Rutherford B. Hayes as well as a message from Confederate President Jefferson Davis telling his congress that the Southern cause was “just and holy.” Classic documents such as Lincoln’s announcement of forthcoming emancipation and the Emancipation Proclamation are here, as are lesser-known but important documents such as Francis Lieber’s 1863 revised law code for war, General Order 100, and Attorney General James Speed’s 1865 opinion supporting the Johnson administration’s decision to try the Lincoln murder conspirators by special military commission and not in the civilian courts.
Each of the selections in <i>Political Arguments<i> is preceded by editor Thomas Mackey’s introductory headnotes that explain the document’s historical significance and trace its lasting impact. These commentaries provide insight into not just law and public policy but also the broad sweep of issues important to Civil War– era Americans.
A Documentary History of the American Civil War Era is an essential acquisition for academic and public libraries in addition to being a valuable resource for courses on the War and Reconstruction, legal history, political history, and nineteenth- century American history.

The first two volumes of the series, Legislative Achievements and Political Arguments, were released last year. The final installments, Judicial Decisions, is split into two volumes, with this one, volume 3, spanning from 1857 to 1866. It contains some of the classic judicial decisions of the time such as the 1857 decision in Dred Scott and the 1861 Ex parte Merryman decision. Other decisions are well known to specialists but deserve wider readership and discussion, such as the October 1859 Jefferson County, Virginia, indictment of John Brown and the decision in the 1864 case of political and seditious activity in Ex parte Vallandigham. These judicial voices constitute a lasting and often overlooked aspect of the age of Abraham Lincoln. Mackey’s headnotes and introductory essays situate cases within their historical context and trace their lasting significance. In contrast to the war, these judicial decisions lasted well past their immediate political and legal moment and deserve continued scholarship and scrutiny.
This document collection presents the raw “stuff” of the Civil War era so that students, scholars, and interested readers can measure and gauge how that generation met Lincoln’s challenge to “think anew, and act anew.” A Documentary History of the American Civil War Era is an essential acquisition for academic and public libraries in addition to being a valuable resource for courses on the Civil War and Reconstruction, legal history, political history, and nineteenth-century American history.
Thomas C. Mackey is a professor of history at the University of Louisville and adjunct Professor of Law at Brandeis School of Law. He is the author of Pornography on Trial and Pursuing Johns.

In 1861 at the age of eighteen, Edward Woolsey Bacon, a Yale student and son of well-known abolitionist minister Leonard Bacon, left his home in New Haven, Connecticut, to fight for the United States. Over the next four years Bacon served in both the Union navy and army, which gave him a sweeping view of the Civil War. His postings included being a captain’s clerk on the USS Iroquois, a hospital clerk in his hometown, a captain in the 29th Connecticut Infantry (Colored), and a major in the 117th U.S. Colored Infantry, and he described these experiences in vibrant letters to his friends and family. Historian George S. Burkhardt has compiled these letters, as well as Bacon’s diary in the impressive Double Duty in the Civil War: The Letters of Sailor and Soldier Edward W. Bacon.
Bacon tells of hunting Confederate commerce raiders on the high seas, enduring the tedium of blockade duty, and taking part in riverine warfare on the Mississippi. He recalls sweating in South Carolina as an infantry officer during drill and picket duty, suffering constant danger in the battlefield trenches of Virginia, marching victoriously on fallen Richmond, and tolerating the boredom of occupation duty in Texas.
His highly entertaining letters shed new light on naval affairs and reveal a close-knit family life. The narrative of his duty with black troops is especially valuable, since few first-hand accounts from white officers of the U.S. Colored Troops exist. Furthermore, his beliefs about race, slavery, and the Union cause were unconventional for the time and stand in contrast to those held by many of his contemporaries.
Double Duty in the Civil War is filled with lively descriptions of the men Bacon met and the events he experienced. With Burkhardt’s careful editing and useful annotations, Bacon’s letters and diary excerpts give rare insight into areas of the Civil War that have been neglected because of a lack of available sources. Given the scarcity of eyewitness testimonies to navy life and life in African American regiments, this book is a rarity indeed.
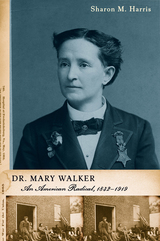
Perhaps more telling about her life are the words of an 1866 London Anglo-American Times reporter, "Her strange adventures, thrilling experiences, important services and marvelous achievements exceed anything that modern romance or fiction has produced. . . . She has been one of the greatest benefactors of her sex and of the human race."
In this biography Sharon M. Harris steers away from a simplistic view and showcases Walker as a Medal of Honor recipient, examining her work as an activist, author, and Civil War surgeon, along with the many nineteenth-century issues she championed:political, social, medical, and legal reforms, abolition, temperance, gender equality, U.S. imperialism, and the New Woman.
Rich in research and keyed to a new generation, Dr. Mary Walker captures its subject's articulate political voice, public self, and the realities of an individual whose ardent beliefs in justice helped shape the radical politics of her time.

From Peoria to Corinth, from Corinth to Vicksburg, up the Red River country, down to Mobile and Fort Blakely, and back to Tupelo and Selma, the 47th marched three thousand miles during Burdette's tour, from March 1862 to December 1864.
In a literate voice rare in war memoirs, Burdette speaks of comradeship built and tested, the noise and confusion of the battlefield, the conflicting feelings of witnessing a military execution. Both nostalgic and piercingly immediate, his remembrances evoke the sights, sounds, smells, and above all the inner feelings stirred up by war, from exuberance to terror and from patriotic fervor to compassion for a fallen enemy.
Originally published--on the eve of another great conflict--in 1914, The Drums of the 47th is a moving depiction of the inner life of the common soldier. Like Stephen Crane's The Red Badge of Courage, Burdette's book puts a human face on the war and his words speak to all who have served or imagined serving under fire. The introduction by John E. Hallwas provides a biographical sketch of Burdette and a commentary on his engaging Civil War memoir.
READERS
Browse our collection.
PUBLISHERS
See BiblioVault's publisher services.
STUDENT SERVICES
Files for college accessibility offices.
UChicago Accessibility Resources
home | accessibility | search | about | contact us
BiblioVault ® 2001 - 2024
The University of Chicago Press









