635 have author last names that start with P have author last names that start with P


For over forty years the Harvard Institute for International Development (HIID) has worked with countries in the developing world on the complex issues of economic and social reform. This volume describes the experience of the Institute in the challenging development assistance world of the 1980s and early 1990s, when HIID's largest projects involved work with countries attempting to move away from high levels of government intervention to more market-friendly systems. These efforts involved work in formerly centrally planned command economies (e.g., Russia, Vietnam, etc.) as well as in the mixed plan/market economies of Asia, Africa, and Latin America. The book also describes HIID's efforts in education and health reform as well as in the rapidly expanding area of environmental economics and policy.
Assisting Development in a Changing World is an unvarnished account written by the HIID practitioners who participated in these programs and edited by its former director and executive directors.



In the decades after the United States formally declared its independence in 1776, Americans struggled to gain recognition of their new republic and their rights as citizens. None had to fight harder than the nation’s seamen, whose labor took them far from home and deep into the Atlantic world. Citizen Sailors tells the story of how their efforts to become American at sea in the midst of war and revolution created the first national, racially inclusive model of United States citizenship.
Nathan Perl-Rosenthal immerses us in sailors’ pursuit of safe passage through the ocean world during the turbulent age of revolution. Challenged by British press-gangs and French privateersmen, who considered them Britons and rejected their citizenship claims, American seamen demanded that the U.S. government take action to protect them. In response, federal leaders created a system of national identification documents for sailors and issued them to tens of thousands of mariners of all races—nearly a century before such credentials came into wider use.
Citizenship for American sailors was strikingly ahead of its time: it marked the federal government’s most extensive foray into defining the boundaries of national belonging until the Civil War era, and the government’s most explicit recognition of black Americans’ equal membership as well. This remarkable system succeeded in safeguarding seafarers, but it fell victim to rising racism and nativism after 1815. Not until the twentieth century would the United States again embrace such an inclusive vision of American nationhood.




When more than twenty million immigrants arrived in the United States between 1880 and 1920, the government attempted to classify them according to prevailing ideas about race and nationality. But this proved hard to do. Ideas about racial or national difference were slippery, contested, and yet consequential—were “Hebrews” a “race,” a “religion,” or a “people”? As Joel Perlmann shows, a self-appointed pair of officials created the government’s 1897 List of Races and Peoples, which shaped exclusionary immigration laws, the wording of the U.S. Census, and federal studies that informed social policy. Its categories served to maintain old divisions and establish new ones.
Across the five decades ending in the 1920s, American immigration policy built increasingly upon the belief that some groups of immigrants were desirable, others not. Perlmann traces how the debates over this policy institutionalized race distinctions—between whites and nonwhites, but also among whites—in immigration laws that lasted four decades.
Despite a gradual shift among social scientists from “race” to “ethnic group” after the 1920s, the diffusion of this key concept among government officials and the public remained limited until the end of the 1960s. Taking up dramatic changes to racial and ethnic classification since then, America Classifies the Immigrants concentrates on three crucial reforms to the American Census: the introduction of Hispanic origin and ancestry (1980), the recognition of mixed racial origins (2000), and a rethinking of the connections between race and ethnic group (proposed for 2020).

“Sitting down with a young and brilliant mathematician, I asked what he thought were his biggest problems in working toward tenure. Instead of describing difficulties with his equations or his software programs, he lamented that (a) his graduate assistant wasn’t completing his tasks on time, (b) his department chair didn’t seem to care if junior faculty obtained grants, and (c) a senior professor kept glaring at him in faculty meetings. He knew he could handle the intellectual side of being an academic—but what about the people side? ‘Why didn’t they offer “Being a Professor 101” in graduate school?’ he wondered.”
Promotion and Tenure Confidential provides that course in an astute and practical book, which shows that P&T is not just about research, teaching, and service but also about human relations and political good sense. Drawing on research and extensive interviews with junior and senior faculty across many institutions, David D. Perlmutter provides clear-sighted guidance on planning and managing an academic career, from graduate school to tenure and beyond.
Topics include:
— Making the transformation from student and protégé to teacher and mentor
— Seeking out and holding onto lifelong allies
— How to manage your online reputation and avoid “death by Google”
— What to say and what not to say to deans and department chairs
— How meeting deadlines wins points with everyone in your life
— How, when, and to whom to say “no”
— When and how to look for a new job when you have a job
— How (and whom) to ask for letters of recommendation
— What to do if you know you’re not going to get tenure

The nineteenth century was the golden age of private life, a time when the tentative self-consciousness of the Renaissance and earlier eras took recognizable form, and the supreme individual, with a political, scientific, and above all existential value, emerged. The present book, fourth in the popular series, chronicles this development from the tumult of the French Revolution to the outbreak of World War I—a century and a quarter of rapid, ungovernable change culminating in a conflict that, at a stroke, altered life in the Western world.
Guided by six eminent historians, we move from the Enlightenment of the eighteenth century, which conceived of man as a noble creature of reason, into nineteenth-century Romanticism with its affirmation of distinctively individual creatures in all their mystery and impulsiveness, exalting intuition as a mode of knowledge. More and more, men and women wanted to sleep alone, to be left alone to read and write, to dress as they pleased, to eat or drink anything they liked, to consort with and love whomever they fancied. Growing democracies advanced those wishes to the status of rights, expanding markets stimulated them, and migration encouraged them. That new frontier, the city, simultaneously weakened family and community constraints, spurred personal ambitions, and attenuated traditional beliefs.
The authors dramatize the nineteenth century’s organized effort to stabilize the boundary between public and private by mooring it to the family, with the father as sovereign. Such chapters as “The Sweet Delights of Home,” “The Family Triumphant,” and “Private Spaces” describe the new domestic ideal of the private dwelling as a refuge from perils and temptations in the public arena, the father as benevolent despot, the wife as contented practitioner of domestic arts, the children as small versions of adults, equipping themselves to follow in their parents’ righteous footsteps. Particularly in England, the middle class was central to the formation of this homely standard, which spread to the working classes through evangelical preaching, utilitarian writings, and economic changes and improvements that resulted in a separation of home and workplace. At the same time, the gentry was transforming castles into country houses, knights into foxhunters, and landowners into gentleman farmers. The domesticating process also expressed itself in hygienic practices (soap, waterclosets, bathtubs), fashions in clothing, and vogues in sports, courtship, and lovemaking.
From the time of the French Revolution, when private or special interests were looked upon as shadowy influences likely to foster conspiracy and treason, through the rapid transformations of the nineteenth century, the authors reveal the more radical forms of modernity that arrived with the twentieth century, with its explosions of trade and technology. Besides the external development of goods and conveniences, the expanses of the psyche were also being reorganized, bringing a new openness about sexuality liberated from procreation and marriage. Feminism, a relatively sporadic movement in the nineteenth century, became a more persistent force, while young people and the avant-garde continued to break the rules and push for change as an end in itself. As always, law lagged behind reality: in practice, more and more people rebelled against communal and family discipline. The declaration of war in 1917 put a hold on some of the flowering of individuality, but the unstoppable trend toward personality nurtured by private life was only temporarily curbed.

Of the nearly five thousand cases presented to the Supreme Court each year, less than 5 percent are granted review. How the Court sets its agenda, therefore, is perhaps as important as how it decides cases. H. W. Perry, Jr., takes the first hard look at the internal workings of the Supreme Court, illuminating its agenda-setting policies, procedures, and priorities as never before. He conveys a wealth of new information in clear prose and integrates insights he gathered in unprecedented interviews with five justices. For this unique study Perry also interviewed four U.S. solicitors general, several deputy solicitors general, seven judges on the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals, and sixty-four former Supreme Court law clerks.
The clerks and justices spoke frankly with Perry, and his skillful analysis of their responses is the mainspring of this book. His engaging report demystifies the Court, bringing it vividly to life for general readers—as well as political scientists and a wide spectrum of readers throughout the legal profession. Perry not only provides previously unpublished information on how the Court operates but also gives us a new way of thinking about the institution. Among his contributions is a decision-making model that is more convincing and persuasive than the standard model for explaining judicial behavior.

Observers often note the glaring contrast between China's stunning economic progress and stalled political reforms. Although sustained growth in GNP has not brought democratization at the national level, this does not mean that the Chinese political system has remained unchanged. At the grassroots level, a number of important reforms have been implemented in the last two decades.
This volume, written by scholars who have undertaken substantial fieldwork in China, explores a range of grassroots efforts--initiated by the state and society alike--intended to restrain arbitrary and corrupt official behavior and enhance the accountability of local authorities. Topics include village and township elections, fiscal reforms, legal aid, media supervision, informal associations, and popular protests. While the authors offer varying assessments of the larger significance of these developments, their case studies point to a more dynamic Chinese political system than is often acknowledged. When placed in historical context--as in the Introduction--we see that reforms in local governance are hardly a new feature of Chinese political statecraft and that the future of these experiments is anything but certain.

In December 1978 the Chinese Communist Party announced dramatic changes in policy for both agriculture and industry that seemed to repudiate the Maoist “road to socialism” in favor of certain “capitalist” tendencies. The motives behind these changes, the nature of the reforms, and their effects upon the economy and political life of countryside and city are here analyzed by five political scientists and five economists. Their assessments of ongoing efforts to implement the new policies provide a timely survey of what is currently happening in China.
Part One delineates the content of agricultural reforms—including decollectivization and the provisions for households to realize private profits—and examines their impact on production, marketing, peasant income, family planning, local leadership, and rural violence. Part Two examines the evolution of industrial reforms, centering on enterprise profit retention, and their impact on political conflict, resource allocation, investment, material and financial flows, industrial structure, and composition of output. Through all ten chapters one theme is conspicuous—the multiple interactions between politics and economics in China’s new directions since the Cultural Revolution.


With their tonsured heads, white faces, and striking cowls, the monkeys might vaguely resemble the Capuchin monks for whom they were named. How they act is something else entirely. They climb onto each other’s shoulders four deep to frighten enemies. They test friendship by sticking their fingers up one another’s noses. They often nurse—but sometimes kill—each other’s offspring. They use sex as a means of communicating. And they negotiate a remarkably intricate network of alliances, simian politics, and social intrigue. Not monkish, perhaps, but as we see in this downright ethnographic account of the capuchins of Lomas Barbudal, their world is as complex, ritualistic, and structured as any society.
Manipulative Monkeys takes us into a Costa Rican forest teeming with simian drama, where since 1990 primatologists Susan Perry and Joseph H. Manson have followed the lives of four generations of capuchins. What the authors describe is behavior as entertaining—and occasionally as alarming—as it is recognizable: the competition and cooperation, the jockeying for position and status, the peaceful years under an alpha male devolving into bloody chaos, and the complex traditions passed from one generation to the next. Interspersed with their observations of the monkeys’ lives are the authors’ colorful tales of the challenges of tropical fieldwork—a mixture so rich that by the book’s end we know what it is to be a wild capuchin monkey or a field primatologist. And we are left with a clear sense of the importance of these endangered monkeys for understanding human behavioral evolution.

In 1753, at the request of the London Jewish community, the Peiham administration passed an act repealing the religious test that prevented Jewish aliens from being naturalized. This act, formally known as the Jewish Naturalization Act, was of negligible practical importance, but political opponents exploited the issue for an upcoming election campaign. The "Jew Bill" became a battle cry that swept across England. The Peiham administration, sensing the political damage that could be caused by the bill, bowed to the clamor and then took the initiative in defeating its own act.
This book is the first thorough account of that notorious but little-understood episode in English history. Using a largely narrative form the author first discusses the position of the Jews in the mid-eighteenth century and explains why they sought and obtained passage of the bill. He then recounts the beginnings of opposition to it and discusses the religious, economic, political, and psychological reasons for the opposition. He describes in detail the propaganda campaign against the bill and the resultant effect on the election.
The author concludes that this was not an isolated explosion of anti-Semitism, but rather a renewal of a long-standing debate over general naturalization policy. He further concludes that Parliament was more sensitive to public opinion than is generally supposed and that the terms "Whig supremacy" or "trusteeship" are not entirely accurate.
The reader will find that this study reveals much of the English political system of that era: the style and structure of parliamentary politics and electioneering; religious attitudes and economic notions; and the methods and ethical and intellectual standards of journalism and political propaganda.


Between 1640 and 1660, England, Scotland, and Ireland faced civil war, invasion, religious radicalism, parliamentary rule, and the restoration of the monarchy. Carla Gardina Pestana offers a sweeping history that systematically connects these cataclysmic events and the development of the infant plantations from Newfoundland to Surinam.
By 1660, the English Atlantic emerged as religiously polarized, economically interconnected, socially exploitative, and ideologically anxious about its liberties. War increased both the proportion of unfree laborers and ethnic diversity in the settlements. Neglected by London, the colonies quickly developed trade networks, especially from seafaring New England, and entered the slave trade. Barbadian planters in particular moved decisively toward slavery as their premier labor system, leading the way toward its adoption elsewhere. When by the 1650s the governing authorities tried to impose their vision of an integrated empire, the colonists claimed the rights of "freeborn English men," making a bid for liberties that had enormous implications for the rise in both involuntary servitude and slavery. Changes at home politicized religion in the Atlantic world and introduced witchcraft prosecutions.
Pestana presents a compelling case for rethinking our assumptions about empire and colonialism and offers an invaluable look at the creation of the English Atlantic world.

In 1654, England’s Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell conceived a plan of breathtaking ambition: the conquest of Spain’s vast American empire. As the first phase of his Western Design, a large expedition sailed to the West Indies, under secret orders to take Spanish colonies. The English Conquest of Jamaica presents entrenched imperial fantasies confronting Caribbean realities. It captures the moment when the revolutionary English state first became a major player in the Atlantic arena.
Although capturing Jamaica was supposed to be only the first step in Cromwell’s scheme, even that relatively modest acquisition proved difficult. The English badly underestimated the myriad challenges they faced, starting with the unexpectedly fierce resistance offered by the Spanish and other residents who tenaciously defended their island. After sixteen long years Spain surrendered Jamaica and acceded to an English presence in the Americas in the 1670 Treaty of Madrid. But by then, other goals—including profit through commerce rather than further conquest—had superseded the vision behind the Western Design.
Carla Gardina Pestana situates Cromwell’s imperial project in the context of an emerging Atlantic empire as well as the religious strife and civil wars that defined seventeenth-century England. Though falling short of its goal, Cromwell’s plan nevertheless reshaped England’s Atlantic endeavors and the Caribbean region as a whole. Long before sugar and slaves made Jamaica Britain’s most valuable colony, its acquisition sparked conflicts with other European powers, opened vast tropical spaces to exploitation by the purportedly industrious English, and altered England’s engagement with the wider world.

An intimate look inside Plymouth Plantation that goes beyond familiar founding myths to portray real life in the settlement—the hard work, small joys, and deep connections to others beyond the shores of Cape Cod Bay.
The English settlement at Plymouth has usually been seen in isolation. Indeed, the colonists gain our admiration in part because we envision them arriving on a desolate, frozen shore, far from assistance and forced to endure a deadly first winter alone. Yet Plymouth was, from its first year, a place connected to other places. Going beyond the tales we learned from schoolbooks, Carla Gardina Pestana offers an illuminating account of life in Plymouth Plantation.
The colony was embedded in a network of trade and sociability. The Wampanoag, whose abandoned village the new arrivals used for their first settlement, were the first among many people the English encountered and upon whom they came to rely. The colonists interacted with fishermen, merchants, investors, and numerous others who passed through the region. Plymouth was thereby linked to England, Europe, the Caribbean, Virginia, the American interior, and the coastal ports of West Africa. Pestana also draws out many colorful stories—of stolen red stockings, a teenager playing with gunpowder aboard ship, the gift of a chicken hurried through the woods to a sickbed. These moments speak intimately of the early North American experience beyond familiar events like the first Thanksgiving.
On the 400th anniversary of the Mayflower landing and the establishment of the settlement, The World of Plymouth Plantation recovers the sense of real life there and sets the colony properly within global history.


The field of development is subject to shifts in paradigms, and it is important to examine systematically how these are realized in actual practice. Two currently favored approaches are participation and indigenous knowledge. In this volume's collected papers, development researchers and practitioners share their ideas and experience on the different forms taken by participation and knowledge, not limited to "indigenous" knowledge, in the practice of development. The "development encounters" they describe took place in sites ranging from villages in the Amazon, India, and southern Africa to research laboratories and corporate boardrooms in central Africa, Latin America, and the United States.
This timely and grounded account of participation and knowledge in the front lines will be of interest to a range of practitioners, analysts, and students of development.


The monumental Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups is the most authoritative single source available on the history, culture, and distinctive characteristics of ethnic groups in the United States. The Dimensions of Ethnicity series is designed to make this landmark scholarship available to everyone in a series of handy paperbound student editions. Selections in this series will include outstanding articles that illuminate the social dynamics of a pluralistic nation or masterfully summarize the experience of key groups. Written by the best-qualified scholars in each field, Dimensions of Ethnicity titles will reflect the complex interplay between assimilation and pluralism that is a central theme of the American experience.
The tightening and loosening of ethnic identity under changing definitions of “Americanism” is emphasized in this volume.
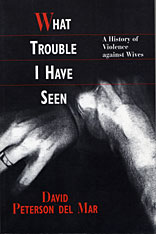
It was 1869 and Sarah Moses, with "a very black eye," told her father: The world will never know what trouble I have seen. What she'd seen was violence at the hands of her husband. Does the world know any more of such things today than it did in Sarah's time?
Sarah, it so happens, lived in Oregon, that Edenic state on the Pacific Coast, and it is here that David Peterson del Mar centers his history of violence against wives. What causes such violence? Has it changed over time? How does it relate to the state of society as a whole? And how have women tried to stop it, resist it, escape it? These are the questions Peterson del Mar pursues, and the answers he finds are as fascinating as they are disturbing.
Thousands of thickly documented divorce cases from the Oregon circuit courts let us listen to voices who often go unheard. These are the people who didn't keep diaries or leave autobiographies, who sometimes could not write at all. Here they speak of a society that quietly condoned wife beating until the spread of an ethos of self-restraint in the late nineteenth century. And then, Peterson del Mar finds, the practice increased with a vengeance with the florescence of expressive individualism during the twentieth century.
What Trouble I Have Seen also traces a dramatic shift in wives' response to their husbands' violence. Settler and Native American women commonly fought abusive mates. Most wives of the late nineteenth century acted more cautiously and relied on others for protection. But twentieth-century privatism, Peterson del Mar discovers, often isolated modern wives from family and neighbors, casting abused women on the mercy of the police, women's shelters, and, most important, their own resources. Thus a new emphasis on self-determination, even as it stimulated violence among men, enhanced the ability of women to resist and escape violent husbands.
The first sustained history of violence toward wives, What Trouble I Have Seen offers remarkable testimony to the impact of social trends on the most private arrangements, and the resilience of women subject to a seemingly timeless crime.

During his invasion of Creek Indian territory in 1813, future U.S. president Andrew Jackson discovered a Creek infant orphaned by his troops. Moved by an “unusual sympathy,” Jackson sent the child to be adopted into his Tennessee plantation household. Through the stories of nearly a dozen white adopters, adopted Indian children, and their Native parents, Dawn Peterson opens a window onto the forgotten history of adoption in early nineteenth-century America. Indians in the Family shows the important role that adoption played in efforts to subdue Native peoples in the name of nation-building.
As the United States aggressively expanded into Indian territories between 1790 and 1830, government officials stressed the importance of assimilating Native peoples into what they styled the United States’ “national family.” White households who adopted Indians—especially slaveholding Southern planters influenced by leaders such as Jackson—saw themselves as part of this expansionist project. They hoped to inculcate in their young charges U.S. attitudes toward private property, patriarchal family, and racial hierarchy.
U.S. whites were not the only ones driving this process. Choctaw, Creek, and Chickasaw families sought to place their sons in white households, to be educated in the ways of U.S. governance and political economy. But there were unintended consequences for all concerned. As adults, these adopted Indians used their educations to thwart U.S. federal claims to their homelands, setting the stage for the political struggles that would culminate in the Indian Removal Act of 1830.

Mark Peterson makes an extraordinary claim in this fascinating book focused around the life and thought of Galileo: it was the mathematics of Renaissance arts, not Renaissance sciences, that became modern science. Galileo's Muse argues that painters, poets, musicians, and architects brought about a scientific revolution that eluded the philosopher-scientists of the day, steeped as they were in a medieval cosmos and its underlying philosophy.
According to Peterson, the recovery of classical science owes much to the Renaissance artists who first turned to Greek sources for inspiration and instruction. Chapters devoted to their insights into mathematics, ranging from perspective in painting to tuning in music, are interspersed with chapters about Galileo's own life and work. Himself an artist turned scientist and an avid student of Hellenistic culture, Galileo pulled together the many threads of his artistic and classical education in designing unprecedented experiments to unlock the secrets of nature.
In the last chapter, Peterson draws our attention to the Oratio de Mathematicae laudibus of 1627, delivered by one of Galileo's students. This document, Peterson argues, was penned in part by Galileo himself, as an expression of his understanding of the universality of mathematics in art and nature. It is "entirely Galilean in so many details that even if it is derivative, it must represent his thought," Peterson writes. An intellectual adventure, Galileo’s Muse offers surprising ideas that will capture the imagination of anyone—scientist, mathematician, history buff, lover of literature, or artist—who cares about the humanistic roots of modern science.


Saving Schools traces the story of the rise, decline, and potential resurrection of American public schools through the lives and ideas of six mission-driven reformers: Horace Mann, John Dewey, Martin Luther King Jr., Albert Shanker, William Bennett, and James Coleman. Yet schools did not become the efficient, egalitarian, and high-quality educational institutions these reformers envisioned. Indeed, the unintended consequences of their legacies shaped today’s flawed educational system, in which political control of stagnant American schools has shifted away from families and communities to larger, more centralized entities—initially to bigger districts and eventually to control by states, courts, and the federal government.
Peterson’s tales help to explain how nation building, progressive education, the civil rights movement, unionization, legalization, special education, bilingual teaching, accountability, vouchers, charters, and homeschooling have, each in a different way, set the stage for a new era in American education.
Now, under the impact of rising cost, coupled with the possibilities unleashed by technological innovation, schooling may be transformed through virtual learning. The result could be a personalized, customized system of education in which families have greater choice and control over their children’s education than at any time since our nation was founded.






For teachers and students of Petrarch, Robert M. Durling’s edition of the poems has become the standard one. Readers have praised the translation as both graceful and accurate, conveying a real understanding of what this difficult poet is saying.
The literalness of the prose translation makes this beautiful book especially useful to students who lack a full command of Italian. And students reading the verse in the original will find here an authoritative text.


In this volume, David R. Slavitt, the distinguished translator and author of more than one hundred works of fiction, poetry, and drama, turns his skills to Il Canzoniere (Songbook) by Petrarch, the most influential poet in the history of the sonnet. In Petrarch’s hands, lyric verse was transformed from an expression of courtly devotion into a way of conversing with one’s own heart and mind. Slavitt renders the sonnets in Il Canzoniere, along with the shorter madrigals and ballate, in a sparkling and engaging idiom and in rhythm and rhyme that do justice to Petrarch’s achievement.
At the center of Il Canzoniere (also known as Rime Sparse, or Scattered Rhymes) is Petrarch’s obsessive love for Laura, a woman Petrarch asserts he first saw at Easter Mass on April 6, 1327, in the church of Sainte-Claire d’Avignon when he was twenty-two. Though Laura was already married, the sight of her woke in the poet a passion that would last beyond her premature death on April 6, 1348, exactly twenty-one years after he first encountered her. Unlike Dante’s Beatrice—a savior leading the poet by the hand toward divine love—Petrarch’s Laura elicits more earthbound and erotic feelings. David Slavitt’s deft new translation captures the nuanced tone of Petrarch’s poems—their joy and despair, and eventually their grief over Laura’s death. Readers of poetry and especially those with an interest in the sonnet and its history will welcome this volume.

This book examines, in rigorous, quantitative detail, the structure of trade between Japan and the United States, tracing the evolution of trade interdependence and the causes of its increasing intensity. It also looks at sectoral differences in interdependence—at the patterns behind changes in the composition of trade and the complex factors that determine how individual sectors of each economy respond to economic change in all the others.
In the first part, the author designs and estimates a multicountry, multisectoral general equilibrium model. The model is operationalized with careful estimates of the parameters that govern demand, production, and trade in both economies. In the second part, the model is employed to explore various aspects of interdependence and commercial policy. Peter Petri's findings indicate, among other things, that the American and Japanese economies are more closely related than one might judge from the size of their trade. As a result of differences in the structures of the two economies, their interdependence is sharply asymmetric, with economic events in the United States having a greater impact on Japan than vice versa. The study also shows that the roots of bilateral conflict can be traced to structural causes, and suggests that recent structural changes may have increased the incentives for protectionism.

How could the West have better prepared for the fall of communism and gained a clearer picture of Russia's new political landscape? By cultivating an awareness, Nicolai Petro argues, of the deep democratic aspirations of the Russian people since Muscovite times. Petro traces the long history of those aspirations, recovering for us an understanding crucial to our formation of successful foreign policy toward Russia.
Expanding the traditional definition of political culture from single thread to continuous historical tapestry, Petro illuminates a reality previously lost to even the most rigorous Sovietology: the fragility of communism. He portrays an abiding "alternative political culture" that tells us Russia indeed possesses a democratic tradition on which its contemporary democracy rests.
Petro's analysis includes many surprising and incisive observations. In a look at the Russian Orthodox Church, he traces its long history of support for opposition sentiment during both tsarist and Soviet times and its support for democracy today. He also explores the character and power of contemporary Russian nationalism and traces its origins to the neo-Slavophile national identity that took its shape as a challenge to Bolshevik oppression. Delineating Russia's postcommunist political parties, the author reveals their roots in prerevolutionary times and explains how this continuity makes Russian political aspirations far more predictable than is commonly assumed.
Awakening us to Russia's historical involvement in the democratic quest that lies at the heart of Western values, Petro opens a path for a more meaningful, more productive understanding of modern Russia.

Petronius (C. or T. Petronius Arbiter), who is reasonably identified with the author of this famous satyric and satiric novel, was a man of pleasure and of good literary taste who flourished in the times of Claudius (4154 CE) and Nero (5468). As Tacitus describes him, he used to sleep by day, and attend to official duties or to his amusements by night. At one time he was governor of the province of Bithynia in Asia Minor and was also a consul, showing himself a man of vigour when this was required. Later he lapsed into indulgence (or assumed the mask of vice) and became a close friend of Nero. Accused by jealous Tigellinus of disloyalty and condemned, with self-opened veins he conversed lightly with friends, dined, drowsed, sent to Nero a survey of Nero's sexual deeds, and so died, 66 CE.
The surviving parts of Petronius's romance Satyricon mix philosophy and real life, prose and verse, in a tale of the disreputable adventures of Encolpius and two companions, Ascyltus and Giton. In the course of their wanderings they attend a showy and wildly extravagant dinner given by a rich freedman, Trimalchio, whose guests talk about themselves and life in general. Other incidents are a shipwreck and somewhat lurid proceedings in South Italy. The work is written partly in pure Latin, but sometimes purposely in a more vulgar style. It parodies and otherwise attacks bad taste in literature, pedantry and hollow society.
Apocolocyntosis, "Pumpkinification" (instead of deification), is probably by Seneca the wealthy philosopher and courtier (ca. 4 BCE65 CE). It is a medley of prose and verse and a political satire on the Emperor Claudius written soon after he died in 54 CE and was deified.

Two rollicking Roman satires.
The Satyrica (Satyricon liber), a comic-picaresque fiction in prose and verse traditionally attributed to the Neronian Petronius (d. AD 66) but possibly of Flavian or Trajanic date, survives only as fragments of a much larger whole. It takes the form of a first-person narrative by the endearing ne’er-do-well Encolpius, a brilliant storyteller, parodist, and mimic who recalls episodes from his past life as a wandering bohemian, living by his wits on the margins of society in Greek southern Italy and encountering a vividly realized array of characters from the early imperial demimonde, including the wealthy freedman Trimalchio, one of the most unforgettable characters in all of Latin literature.
Paired with the Satyrica, and likewise in prose and verse, is the Apocolocyntosis (Pumpkinification), a short satirical pamphlet lampooning the death, apotheosis, and attempt to enter heaven of the emperor Claudius (reigned 41–54). If the work of Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC–AD 65), better known for his austere Stoic moralism, its sarcastic wit and rollicking humor were no doubt inspired by bitterness over his exile at Claudius’ hands in 41–49.
For this Loeb edition the Latin texts have been freshly edited and translated, with ample introductions and explanatory notes.

As scholars have remarked, the word kleos in the Iliad and the Odyssey alike refers to something more substantive and complex than “fame” or “glory.” Kleos distinctly supposes an oral narrative—principally an “oral history,” a “life story” or ultimately an “oral tradition.” When broken down into its twin constituents, “words” and “actions” or “deeds,” a hero’s kleos serves to define him as a fully gendered social being.
This book is a meditation on this concept as expressed and experienced in the adult society Telemachos find himself in. Kleos is the yardstick by which his psychological change was appreciated by Homer’s audiences. As this book shows through philological and interdisciplinary analysis, Prince Telemachos grows up in the course of the Telemachy and arguably even beyond (in book 24): his education, which is conceived largely as an apprenticeship on land and sea, admits him gradually if unevenly to a full-fledged adult kleos—a kleos that nonetheless necessarily remains minor in comparison to that of his father and other elders.

Henry Petroski’s previous bestsellers have delighted readers with intriguing stories about the engineering marvels around us, from the lowly pencil to the soaring suspension bridge. In this book, Petroski delves deeper into the mystery of invention, to explore what everyday artifacts and sophisticated networks can reveal about the way engineers solve problems.
Engineering entails more than knowing the way things work. What do economics and ecology, aesthetics and ethics, have to do with the shape of a paper clip, the tab of a beverage can, the cabin design of a turbojet, or the course of a river? How do the idiosyncrasies of individual engineers, companies, and communities leave their mark on projects from Velcro® to fax machines to waterworks? Invention by Design offers an insider’s look at these political and cultural dimensions of design and development, production and construction.
Readers unfamiliar with engineering will find Petroski’s enthusiasm contagious, whether the topic is the genesis of the Ziploc® baggie or the averted collapse of Manhattan’s sleekest skyscraper. And those who inhabit the world of engineering will discover insights to challenge their customary perspective, whether their work involves failure analysis, systems design, or public relations. Written with the flair that readers have come to expect from his books, Invention by Design reaffirms Petroski as the master explicator of the principles and processes that turn thoughts into the many things that define our made world.

When planes crash, bridges collapse, and automobile gas tanks explode, we are quick to blame poor design. But Henry Petroski says we must look beyond design for causes and corrections. Known for his masterly explanations of engineering successes and failures, Petroski here takes his analysis a step further, to consider the larger context in which accidents occur.
In To Forgive Design he surveys some of the most infamous failures of our time, from the 2007 Minneapolis bridge collapse and the toppling of a massive Shanghai apartment building in 2009 to Boston's prolonged Big Dig and the 2010 Gulf oil spill. These avoidable disasters reveal the interdependency of people and machines within systems whose complex behavior was undreamt of by their designers, until it was too late. Petroski shows that even the simplest technology is embedded in cultural and socioeconomic constraints, complications, and contradictions.
Failure to imagine the possibility of failure is the most profound mistake engineers can make. Software developers realized this early on and looked outside their young field, to structural engineering, as they sought a historical perspective to help them identify their own potential mistakes. By explaining the interconnectedness of technology and culture and the dangers that can emerge from complexity, Petroski demonstrates that we would all do well to follow their lead.

The monumental Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups is the most authoritative single source available on the history, culture, and distinctive characteristics of ethnic groups in the United States. The Dimensions of Ethnicity series is designed to make this landmark scholarship available to everyone in a series of handy paperbound student editions. Selections in this series will include outstanding articles that illuminate the social dynamics of a pluralistic nation or masterfully summarize the experience of key groups.
Written by the best-qualified scholars in each field, Dimensions of Ethnicity titles will reflect the complex interplay between assimilation and pluralism that is a central theme of the American experience.
In Prejudice, the history and psychology of discriminatory policies is contrasted with efforts to overcome discrimination.

When the American reporter Henry Morton Stanley stepped out of the jungle in 1871 and doffed his pith helmet to the Scottish missionary-explorer Dr. David Livingstone, his greeting was to take on mythological proportions. But do any of us really know what his words meant at the time--and what they have come to mean since?
Far from meeting in a remote thicket in "Darkest Africa," Stanley met Livingstone in the middle of a thriving Muslim community. The news of their encounter was transmitted around the globe, and Livingstone instantly became one of the world's first international celebrities.
This book shows how urgently a handshake between a Briton and an American was needed to heal the rift between the two countries after the American Civil War. It uncovers for the first time the journeys that Livingstone's African servants made around Britain after his death, and it makes a case for Stanley's immense influence on the idea of the modern at the dawn of the twentieth century. Drawing on films, children's books, games, songs, cartoons, and TV shows, this book reveals the many ways our culture has remembered Stanley's phrase, while tracking the birth of an Anglo-American Christian imperialism that still sets the world agenda today.
Dr. Livingstone, I Presume? is a story of conflict and paradox that also takes us into the extraordinary history of British engagement with Africa. Clare Pettitt shows both the bleakest side of imperialism and the strange afterlife of a historical event in popular mythmaking and music hall jokes.

Ancient Sardis, the capital of Lydia, was of outstanding importance: in the Lydian period it held the residence of the kings and subsequently, under Persian rule, the satraps. Throughout antiquity it remained an administrative center. Travelers of modern times and archaeological excavations have revealed, from the city site and its surroundings, inscriptions written mostly in Greek, some in Latin. Their texts deal with all kinds of subjects: decrees, public honors, civil and sacred laws, letters, epitaphs, and more.
In the corpus “Sardis VII 1” (1932) W. H. Buckler and D. M. Robinson published all inscriptions (228 items) known up to 1922, after which year excavation at Sardis came to a halt because of the Greek-Turkish war. Since excavation resumed in 1958, a portion of the Greek and Latin inscriptions has been published in various, widely scattered places; another portion, containing important texts discovered during the last ten years, was until now unpublished. The aim of this monograph is to present in a comprehensive corpus the entire epigraphic harvest (485 items) made in Sardis and its territory since 1958. Each inscription is accompanied by a description of the monument, bibliography, translation, and commentary; indices, concordances, photographs, and maps complement the collection.

Arousal is fundamental to all cognition. It is intuitively obvious, absolutely necessary, but what exactly is it? In Brain Arousal and Information Theory, Donald Pfaff presents a daring perspective on this long-standing puzzle. Pfaff argues that, beneath our mental functions and emotional dispositions, a primitive neuronal system governs arousal. Employing the simple but powerful framework of information theory, Pfaff revolutionizes our understanding of arousal systems in the brain.
Starting with a review of the neuroanatomical, neurophysiological, and neurochemical components of arousal, Pfaff asks us to look at the gene networks and neural pathways underlying the brain’s arousal systems much as a design engineer would contemplate information systems. This allows Pfaff to postulate that there is a bilaterally symmetric, bipolar system universal among mammals that readies the animal or the human being to respond to stimuli, initiate voluntary locomotion, and react to emotional challenges. Applying his hypothesis to heightened states of arousal—sex and fear—Pfaff shows us how his theory opens new scientific approaches to understanding the structure of brain arousal.
A major synthesis of disparate data by a preeminent neuroscientist, Brain Arousal and Information Theory challenges current thinking about cognition and behavior. Whether you subscribe to Pfaff’s theory or not, this book will stimulate debate about the nature of arousal itself.

Throughout his remarkable career, Donald Pfaff has demonstrated that by choosing problems and methods with care, biologists can study the molecular mechanisms of brains more complex than those of fruit flies, snails, roundworms, and other invertebrates. His half century in the lab, starting with his discovery of hormone receptors in the brains of mammals and leading to the first detailed account of a neural circuit for mammalian behavior, puts him in a unique position to survey the origins and development of behavioral neurobiology and the current state of research. How the Vertebrate Brain Regulates Behavior offers a close-up, conversational perspective on scientific struggles and successes throughout a fifty-year quest to understand how behavior is regulated in a complex organism.
In graduate school, when Pfaff expressed a desire to study behavioral regulation, his advisor suggested focusing on hormones. Pfaff’s investigation into the hormonal basis of female sexual behavior in laboratory rats led him to a comprehensive appreciation of how hormone-dependent neurons work through neural circuits to produce discrete behaviors among all vertebrates. This breakthrough, along with other researchers’ findings, established a link between molecular biology and neuroscience that opened up a fruitful new field of inquiry.
Pfaff’s approach is to focus on one solvable problem and explore it from many angles. He begins with a single observed behavior and traces its regulation through a series of biological mechanisms—from hormones to genes to neural circuits. Pfaff’s relentless pursuit of his goals continues to inspire neuroscientists today.


Praised as "one of those rare scientific books that can be read both for pleasure and instruction" when it was first published, The Life of Yeasts now appears in a new edition incorporating the exciting developments of the last decade. Nowhere else is there an introduction to this complex group of organisms that is as succinct, clear, and useful. Reviewing the first edition in Nature, A. H. Cook welcomed it as a "simple but wide-ranging account of a field which for various reasons has hitherto mostly been described only in a few specialized texts or in many respects only piecemeal in original publications."
This book is written for the nonspecialist who wishes to understand the yeasts, but not necessarily to become an expert on them. The new edition covers recent and major advances in the morphology, physiology, genetics, and ecology of these organisms, which have long been important in commerce and medicine and are ever more studied in the laboratory as prototypical eukaryotes.


Dissatisfied with the explanations of the business cycle provided by the Keynesian, monetarist, New Keynesian, and real business cycle schools, Edmund Phelps has developed from various existing strands—some modern and some classical—a radically different theory to account for the long periods of unemployment that have dogged the economies of the United States and Western Europe since the early 1970s. Phelps sees secular shifts and long swings of the unemployment rate as structural in nature. That is, they are typically the result of movements in the natural rate of unemployment (to which the equilibrium path is always tending) rather than of long-persisting deviations around a natural rate itself impervious to changing structure. What has been lacking is a “structuralist” theory of how the natural rate is disturbed by real demand and supply shocks, foreign and domestic, and the adjustments they set in motion.
To study the determination of the natural rate path, Phelps constructs three stylized general equilibrium models, each one built around a distinct kind of asset in which firms invest and which is important for the hiring decision. An element of these models is the modern economics of the labor market whereby firms, in seeking to dampen their employees’ propensities to quit and shirk, drive wages above market-clearing levels-the phenomenon of the “incentive wage”—and so generate involuntary unemployment in labor-market equilibrium. Another element is the capital market, where interest rates are disturbed by demand and supply shocks such as shifts in profitability, thrift, productivity, and the rate of technical progress and population increase. A general-equilibrium analysis shows how various real shocks, operating through interest rates upon the demand for employees and through the propensity to quit and shirk upon the incentive wage, act upon the natural rate (and thus equilibrium path).
In an econometric and historical section, the new theory of economic activity is submitted to certain empirical tests against global postwar data. In the final section the author draws from the theory some suggestions for government policy measures that would best serve to combat structural slumps.

Nobel Laureate Edmund Phelps and an international group of economists argue that economic health depends on the widespread presence of certain values, in particular individualism and self-expression.
Nobel Laureate Edmund Phelps has long argued that the high level of innovation in the lead nations of the West was never a result of scientific discoveries plus entrepreneurship, as Schumpeter thought. Rather, modern values—particularly the individualism, vitalism, and self-expression prevailing among the people—fueled the dynamism needed for widespread, indigenous innovation. Yet finding links between nations’ values and their dynamism was a daunting task. Now, in Dynamism, Phelps and a trio of coauthors take it on.
Phelps, Raicho Bojilov, Hian Teck Hoon, and Gylfi Zoega find evidence that differences in nations’ values matter—and quite a lot. It is no accident that the most innovative countries in the West were rich in values fueling dynamism. Nor is it an accident that economic dynamism in the United States, Britain, and France has suffered as state-centered and communitarian values have moved to the fore.
The authors lay out their argument in three parts. In the first two, they extract from productivity data time series on indigenous innovation, then test the thesis on the link between values and innovation to find which values are positively and which are negatively linked. In the third part, they consider the effects of robots on innovation and wages, arguing that, even though many workers may be replaced rather than helped by robots, the long-term effects may be better than we have feared. Itself a significant display of creativity and innovation, Dynamism will stand as a key statement of the cultural preconditions for a healthy society and rewarding work.


A Financial Times Book of the Year
A ProMarket Book of the Year
“Superbly argued and important…Donald Trump is in so many ways a product of the defective capitalism described in The Great Reversal. What the U.S. needs, instead, is another Teddy Roosevelt and his energetic trust-busting. Is that still imaginable? All believers in the virtues of competitive capitalism must hope so.”
—Martin Wolf, Financial Times
“In one industry after another…a few companies have grown so large that they have the power to keep prices high and wages low. It’s great for those corporations—and bad for almost everyone else.”
—David Leonhardt, New York Times
“Argues that the United States has much to gain by reforming how domestic markets work but also much to regain—a vitality that has been lost since the Reagan years…His analysis points to one way of making America great again: restoring our free-market competitiveness.”
—Arthur Herman, Wall Street Journal
Why are cell-phone plans so much more expensive in the United States than in Europe? It seems a simple question, but the search for an answer took one of the world’s leading economists on an unexpected journey through some of the most hotly debated issues in his field. He reached a surprising conclusion: American markets, once a model for the world, are giving up on healthy competition.
In the age of Silicon Valley start-ups and millennial millionaires, he hardly expected this. But the data from his cutting-edge research proved undeniable. In this compelling tale of economic detective work, we follow Thomas Philippon as he works out the facts and consequences of industry concentration, shows how lobbying and campaign contributions have defanged antitrust regulators, and considers what all this means. Philippon argues that many key problems of the American economy are due not to the flaws of capitalism or globalization but to the concentration of corporate power. By lobbying against competition, the biggest firms drive profits higher while depressing wages and limiting opportunities for investment, innovation, and growth. For the sake of ordinary Americans, he concludes, government needs to get back to what it once did best: keeping the playing field level for competition. It’s time to make American markets great—and free—again.

Like other dangerous but pleasurable activities, such as downhill skiing and mountain climbing, engaging in unprotected sex implicitly involves the weighing of costs and benefits. Recognizing that the transmission of the AIDS virus is a consequence of private choices—rational and often informed—to engage in risky conduct, the authors employ tools of economic analysis to reassess the orthodox approach to AIDS by the public health community.
Standard predictions of the spread of AIDS, the authors argue, are questionable because they ignore rational behavioral response to the risk of infection. For the same reason, customary recommended public health measures, such as extensive testing for the AIDS virus, not only may be ineffective in controlling the spread of the disease but may actually cause it to spread more rapidly. The authors examine regulatory measures and proposals such as mandatory testing, criminal punishments, and immigration controls, as well as the subsidization of AIDS education and medical research, the social and fiscal costs of AIDS, the political economy of the government's response, and the interrelation of AIDS and fertility risk.
Neither liberal nor conservative, yet on the whole skeptical about governmental involvement in the epidemic, this book is certain to be controversial, but its injection of hard-headed economic thinking into the AIDS debate is long overdue. Although Private Choices and Public Health is accessible to the interested general reader, it will also capture the attention of economists—especially those involved in health issues—epidemiologists, public health workers, lawyers, and specialists in sexual behavior and drug addiction.

People tend to flirt only with serious things--madness, disaster, other people's affections. So is flirtation dangerous, exploiting the ambiguity of promises to sabotage our cherished notions of commitment? Or is it, as Adam Phillips suggests, a productive pleasure, keeping things in play, letting us get to know them in different ways, allowing us the fascination of what is unconvincing? This is a book about the possibilities of flirtation, its risks and instructive amusements--about the spaces flirtation opens in the stories we tell ourselves, particularly within the framework of psychoanalysis.
Phillips looks at life as a tale to be told but rejects the idea of a master plot. Instead, he says, we should be open to the contingent, and flirtation shows us the way. His book observes children flirting with their parents, our various selves flirting with one another, and literature flirting with psychoanalysis. As Phillips explores the links between literature and psychoanalysis--ranging from Philip Roth to Isaac Rosenberg, Karl Kraus to John Clare--psychoanalysis emerges as a multi-authored autobiography. Its subjects are love, loss, and memory; its authors are the analyst and the analysand, as well as the several selves brought to life in the process. A passionate and delightfully playful defense of the virtues of being uncommitted, On Flirtation sets before us the virtue of a yet deeper commitment to the openendedness of our life stories.

In a style that is writerly and audacious, Adam Phillips takes up a variety of seemingly ordinary subjects underinvestigated by psychoanalysis--kissing, worrying, risk, solitude, composure, even farting as it relates to worrying.
He argues that psychoanalysis began as a virtuoso improvisation within the science of medicine, but that virtuosity has given way to the dream of science that only the examined life is worth living. Phillips goes on to show how the drive to omniscience has been unfortunate both for psychoanalysis and for life. He reveals how much one's psychic health depends on establishing a realm of life that successfully resists examination.

Iris Murdoch once suggested that to understand any philosopher's work we must ask what he or she is frightened of. To understand any psychoanalyst's work--both as a clinician and as a writer--we should ask what he or she loves, because psychoanalysis is about the unacceptable and about love, two things that we may prefer to keep apart, but that Freud found to be inextricable. If it is possible to talk about psychoanalysis as a scandal, without spuriously glamorizing it, then one way of doing it is simply to say that Freud discovered that love was compatible, though often furtively, with all that it was meant to exclude. There are, in other words--and most of literature is made up of these words--no experts on love. And love, whatever else it is, is terror.
In a manner characteristically engaging and challenging, charming and maddening, Adam Phillips teases out the complicity between desire and the forbidden, longing and dread. His book is a chronicle of that all-too-human terror, and of how expertise, in the form of psychoanalysis, addresses our fears--in essence, turns our terror into meaning.
It is terror, of course, that traditionally drives us into the arms of the experts. Phillips takes up those topics about which psychoanalysis claims expertise--childhood, sexuality, love, development, dreams, art, the unconscious, unhappiness--and explores what Freud's description of the unconscious does to the idea of expertise, in life and in psychoanalysis itself. If we are not, as Freud's ideas tell us, masters of our own houses, then what kind of claims can we make for ourselves? In what senses can we know what we are doing? These questions, so central to the human condition and to the state of psychoanalysis, resonate through this book as Phillips considers our notions of competence, of a professional self, of expertise in every realm of life from parenting to psychoanalysis. Terrors and Experts testifies to what makes psychoanalysis interesting, to that interest in psychoanalysis--which teaches us the meaning of our ignorance--that makes the terrors of life more bearable, even valuable.

Although he founded no school of his own, D. W. Winnicott (1896–1971) is now regarded as one of the most influential contributors to psychoanalysis since Freud. In over forty years of clinical practice, he brought unprecedented skill and intuition to the psychoanalysis of children. This critical new work by Adam Phillips presents the best short introduction to the thought and practice of Winnicott that is currently available.
Winnicott’s work was devoted to the recognition and description of the good mother and the use of the mother–infant relationship as the model of psychoanalytic treatment. His belief in natural development became a covert critique of overinterpretative methods of psychoanalysis. He combined his idiosyncratic approach to psychoanalysis with a willingness to make his work available to nonspecialist audiences. In this book Winnicott takes his place with Melanie Klein and Jacques Lacan as one of the great innovators within the psychoanalytic tradition.

"At its peak in the late sixteenth century," this history begins, "Spain controlled the first empire upon which the sun never set and exercised a tremendous influence in European affairs. By 1600, thoughtful Spaniards knew that something had gone terribly wrong, and by 1650 the rest of Europe knew it too."
By focusing on one Castilian city, Ciudad Real, Carla Rahn Phillips seeks to shed light on the mysterious downfall of Spanish power. Looking first at the general history of the city and region, she goes on to examine population, agriculture, industry, taxation, and elite patterns of investment. She shows how Ciudad Real's economy grew from about 1500 to 1580, faltered and stagnated through most of the seventeenth century, and reestablished a subsistence economy around 1750. Self-contained though Ciudad Real was, its history illuminates economic and social change during Spain's Golden Age.


The Diehards is a study of the 112 peers who voted against the Parliament Bill of 1911. In voting against this bill, which abolished the veto power of the House of Lords, the diehards defied the leadership of their own party. Other Unionists were willing to capitulate in response to the Liberal government's threat to create enough new peers to swamp the upper chamber, but the diehards were ready to “die in the last ditch.”
There has never been a satisfactory explanation of diehard intransigence. A mistake of contemporaries and of later historians has been to characterize the diehards as “backwoodsmen” who cared little about national politics and barely knew their way to the House of Lords. But in fact, as Gregory Phillips shows, they were among the most politically active members of the peerage. They can be seen as radical conservatives, willing to countenance drastic changes in certain aspects of politics and society in order to preserve as much as possible of their traditional position and way of life.
Utilizing a wide range of public and private papers, Phillips has given us an economic, social, and political study of Edwardian England that substantially alters our understanding of this crisis in British constitutional history.

The Craig Mound at Spiro, Oklahoma was the richest source of pre-Columbian shell engravings in North America, a treasury of early native American artistry. From about 1250 AD until the early part of this century, it remained virtually undisturbed, but in 1933, it was plundered by commercial diggers. The fragments of the shell cups and gorgets became widely scattered, as museums and private collectors sought to acquire them. It is only through the publication of this work that the pieces have been put back together.
These lavishly illustrated volumes showcase the variety of iconography and of the engravers.


Unequaled in North America as a single source of prehistoric figurative and decorative art, the Craig burial mound was plundered by commercial diggers in 1933. Hundreds of fragile shell artifacts covered with engraved designs were quickly sold and, whole or fragmented, were scattered in public and private collections across the country.
For the past ten years, Dr. Philip Phillips, Honorary Curator of Southeastern Archaeology at Harvard, has supervised a massive project that has involved making rubbings and line drawings of this whole corpus of Southeastern Indian art, matching hundreds of fragments, and classifying the engraved designs by schools.
Volume VI, the last volume of the set, deals with the final phase of the Craig style, then concludes with a summary of the study, a bibliography, and an extensive index.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

A diplomatic mission to the emperor Caligula.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Syncretistic exegesis.
The philosopher Philo was born about 20 BC to a prominent Jewish family in Alexandria, the chief home of the Jewish Diaspora as well as the chief center of Hellenistic culture; he was trained in Greek as well as Jewish learning. In attempting to reconcile biblical teachings with Greek philosophy he developed ideas that had wide influence on Christian and Jewish religious thought.
The Loeb Classical Library edition of the works of Philo is in ten volumes and two supplements, distributed as follows. Volume I: Creation; Interpretation of Genesis II and III. II: On the Cherubim; The Sacrifices of Abel and Cain; The Worse Attacks the Better; The Posterity and Exile of Cain; On the Giants. III: The Unchangeableness of God; On Husbandry; Noah's Work as a Planter; On Drunkenness; On Sobriety. IV: The Confusion of Tongues; The Migration of Abraham; The Heir of Divine Things; On the Preliminary Studies. V: On Flight and Finding; Change of Names; On Dreams. VI: Abraham; Joseph; Moses. VII: The Decalogue; On Special Laws Books I–III. VIII: On Special Laws Book IV; On the Virtues; Rewards and Punishments. IX: Every Good Man Is Free; The Contemplative Life; The Eternity of the World; Against Flaccus; Apology for the Jews; On Providence. X: On the Embassy to Gaius; indexes. Supplement I: Questions on Genesis. II: Questions on Exodus; index to supplements.

Artful descriptions.
This volume presents kindred works important for evidence relating to late Greek art. They are attributed to two men each known as Philostratus and to a third man called Callistratus, otherwise unknown. To an elder Philostratus, the Lemnian, born ca. AD 190, junior kinsman of the Philostratus who wrote the Life of Apollonius of Tyana and Lives of the Sophists, is attributed the series of sixty-five Eikones or Imagines, descriptions (in two books) ostensibly of paintings in a gallery at Naples. A younger Philostratus, apparently his grandson, is credited with seventeen similar descriptions. The fourteen Ekphraseis attributed to Callistratus are descriptions of statues in stone or bronze, written probably in the fourth century AD. It is not known to what extent the descriptions are of real works of art, but they show how artists treated their subjects, and are written with some artistic knowledge. Yet rhetorical skill dominates: these pieces were written to display the writers’ powers of description.

THIS EDITION HAS BEEN REPLACED BY A NEWER EDITION.
Novel and biography are joined in this literary work with a historical core. Philostratus' life of the first century mystic from Tyana was written at the request of the empress Julia Domna. It portrays a man with supernatural powers, a Pythagorean who predicts the future, cures the sick, raises the dead, and himself prevails over death, ascending to heaven and later appearing to disciples to prove his immortality. The account has a rich and varied setting: Apollonius' ministering carries him throughout the eastern Mediterranean world, as far south as Ethiopia, and eastward to India. Philostratus' Life of Apollonius was long viewed by Christians as a dangerous attempt to set up a Christ-like rival.
This two-volume edition of the Life of Apollonius of Tyana includes, in the second volume, a collection of Apollonius' letters and a treatise by the Christian bishop and historian Eusebius attacking Apollonius as a charlatan.
Also available by Philostratus 'the Athenian' in the Loeb Classical Library is his Lives of the Sophists, a treasury of information about notable sophists that yields a good picture of the predominant influence of Sophistic in the educational, social, and political life of the Empire in the 2nd and 3rd centuries.

THIS EDITION HAS BEEN REPLACED BY A NEWER EDITION.
Novel and biography are joined in this literary work with a historical core. Philostratus' life of the first century mystic from Tyana was written at the request of the empress Julia Domna. It portrays a man with supernatural powers, a Pythagorean who predicts the future, cures the sick, raises the dead, and himself prevails over death, ascending to heaven and later appearing to disciples to prove his immortality. The account has a rich and varied setting: Apollonius' ministering carries him throughout the eastern Mediterranean world, as far south as Ethiopia, and eastward to India. Philostratus' Life of Apollonius was long viewed by Christians as a dangerous attempt to set up a Christ-like rival.
This two-volume edition of the Life of Apollonius of Tyana includes, in the second volume, a collection of Apollonius' letters and a treatise by the Christian bishop and historian Eusebius attacking Apollonius as a charlatan.
Also available by Philostratus 'the Athenian' in the Loeb Classical Library is his Lives of the Sophists, a treasury of information about notable sophists that yields a good picture of the predominant influence of Sophistic in the educational, social, and political life of the Empire in the 2nd and 3rd centuries.

Two sophists on the history of sophistry.
Flavius Philostratus, known as “the Elder” or “the Athenian,” was born to a distinguished family with close ties to Lesbos in the later second century, and died around the middle of the third. A sophist who studied at Athens and later lived in Rome, Philostratus provides in Lives of the Sophists a treasury of information about notable practitioners. His sketches of sophists in action paint a fascinating picture of their predominant influence in the educational, social, and political life of the Empire in his time. He is almost certainly the author also of the Life of Apollonius of Tyana (LCL 16, 17, 458) and Heroicus and Gymnasticus (LCL 521).
Eunapius (ca. 345–415) was born in Sardis but studied and spent much of his life in Athens as a sophist and historian. His Lives of Philosophers and Sophists covers figures of personal or intellectual significance to him in the period from Plotinus (ca. 250) to Chrystanthus (ca. 380), including one remarkable woman, Sosipatra, and then focuses on Iamblichus and his students. The work’s underlying rationale combines personal devotion to teachers and colleagues with a broader attempt to rehabilitate Hellenic cultural icons against the rise of Christianity and the influence of its representatives.
This edition of Philostratus and Eunapius thoroughly revises the original edition by Wilmer C. Wright (1921) in light of modern scholarship.

Of the distinguished Lemnian family of Philostrati, Flavius Philostratus 'the Athenian', ca. 170205 CE, was a Greek sophist who studied at Athens and later lived in Rome. He was author of the admirable Life of Apollonius of Tyana (Loeb nos. 16 and 17) and of Lives of the Sophists, a treasury of information about notable sophists. Philostratus's sketches of sophists in action yield a fascinating picture of the predominant influence of Sophistic in the educational, social, and political life of the Empire in the second and third centuries.
The Greek sophist and historian Eunapius was born at Sardis in 347 CE, but went to Athens to study and lived much of his life there teaching rhetoric and possibly medicine. He was initiated into the mysteries and was hostile to Christians. His Lives of Philosophers and Sophists (mainly contemporary with himself) is our only source for knowledge of Neo-Platonism in the latter part of the fourth century.

The life and miracles of a pagan holy man.
This biography of a first-century AD holy man has become one of the most widely discussed literary works of later antiquity. In a grandly baroque style style Philostratus portrays a charismatic teacher and religious reformer from Tyana in Cappadocia (modern central Turkey) who travels the length of the known world, from the Atlantic to the river Ganges. His miracles, which include extraordinary cures and mysterious disappearances, together with his apparent triumph over death, caused pagans to make Apollonius a rival to Jesus of Nazareth.
In his three-volume Loeb edition of this third-century work, Christopher Jones gives a much improved Greek text and an elegant translation with full explanatory notes. The Life of Apollonius is formally a biography (by far the longest that survives from antiquity), but in reality a combination of travel narrative, rhetorical showpiece, and much else. In the introduction, Jones addresses the question of how far the Life is history and how far fiction. He also discusses the survival and reception of the work through Late Antiquity and up to modern times, and the role that it continues to play in controversies about Christianity.

The life and miracles of a pagan holy man.
This biography of a first-century AD holy man has become one of the most widely discussed literary works of later antiquity. In a grandly baroque style style Philostratus portrays a charismatic teacher and religious reformer from Tyana in Cappadocia (modern central Turkey) who travels the length of the known world, from the Atlantic to the river Ganges. His miracles, which include extraordinary cures and mysterious disappearances, together with his apparent triumph over death, caused pagans to make Apollonius a rival to Jesus of Nazareth.
In his three-volume Loeb edition of this third-century work, Christopher Jones gives a much improved Greek text and an elegant translation with full explanatory notes. The Life of Apollonius is formally a biography (by far the longest that survives from antiquity), but in reality a combination of travel narrative, rhetorical showpiece, and much else. In the introduction, Jones addresses the question of how far the Life is history and how far fiction. He also discusses the survival and reception of the work through Late Antiquity and up to modern times, and the role that it continues to play in controversies about Christianity.

The life and miracles of a pagan holy man.
Philostratus' colorful biography of Apollonius of Tyana, recounting the sayings and miracles of a Pythagorean sage, incidentally provoked a long-lasting debate between pagans and Christians. This volume, which completes the Loeb Classical Library edition of the Life of Apollonius of Tyana, provides full context for that much discussed third-century portrayal of a charismatic religious teacher.
Here is a new translation of the surviving letters of Apollonius, augmented and illuminated by recent discoveries. These letters reveal Apollonius' personality and his religious and philosophical ideas. New for this edition is a selection of ancient reports about Apollonius from authors such as St. Jerome and St. Augustine.
Philostratus' biography was quickly caught up in the religious struggles that marked the rise of Christianity. An official in Diocletian's empire named Hierocles used it as ammunition in an anti-Christian polemic, initiating a controversy that lasted well into modern times. The reply by Eusebius, the fourth-century bishop of Caesarea, was originally included in editions of the Life of Apollonius in order to serve as a spiritual antidote and to provide cover for the publishers; today it is an essential chapter in the history of Philostratus' masterpiece.

How to cultivate Greek heroes and athletes.
In the writings of Philostratus (ca. AD 170-ca. 250), the renaissance of Greek literature in the second century AD reached its height. His Life of Apollonius of Tyana, Lives of the Sophists, and Imagines reconceive in different ways Greek religion, philosophy, and art in and for the world of the Roman Empire. In this volume, Heroicus and Gymnasticus, two works of equal creativity and sophistication, together with two brief Discourses (Dialexeis), complete the Loeb edition of his writings.
Heroicus is a conversation in a vineyard amid ruins of the Protesilaus shrine (opposite Troy on the Hellespont), between a wise and devout vinedresser and an initially skeptical Phoenician sailor, about the beauty, continuing powers, and worship of the Homeric heroes. With information from his local hero, the vinedresser reveals unknown stories of the Trojan campaign especially featuring Protesilaus and Palamedes, and describes complex, miraculous, and violent rituals in the cults of Achilles.
Gymnasticus is the sole surviving ancient treatise on sports. It reshapes conventional ideas about the athletic body and expertise of the athletic trainer and also explores the history of the Olympic Games and other major Greek athletic festivals, portraying them as distinctive venues for the display of knowledge.

This book explores how the processes and practices of politics shape political values, such as liberty, justice, equality, and democracy. Mining the history of political episodes and political thinkers, including Caesar and Machiavelli, Mark Philp argues that it is through political activity that "values are articulated and embraced, and they become powerful motivating forces."
Political Conduct is thus an attempt to inform and enrich political theory--to show that its principles would be more relevant to actual politics if they were immersed in history and practice. Philp argues for a separation between moral and political philosophy and proposes that a less abstract and ideal approach to political philosophy than that provided by Rawls, Dworkin, Nagel, and Cohen would be more useful in illuminating the conduct of politicians and the limitations on what they can achieve.

Empires on the Waterfront offers a new spatial framework for understanding Japan’s extended transition into the modern world of nation-states. This study examines a largely unacknowledged system of “special trading ports” that operated under full Japanese jurisdiction in the shadow of the better-known treaty ports. By allowing Japan to circumvent conditions imposed on treaty ports, the special trading ports were key to achieving autonomy and regional power.
Catherine L. Phipps uses an overtly geographic approach to demonstrate that the establishment of Japan’s maritime networks depended on initiatives made and carried out on multiple geographical scales—global, national, and local. The story of the special trading ports unfolds in these three dimensions. Through an in-depth assessment of the port of Moji in northern Kyushu, Empires on the Waterfront recasts the rise of Japan’s own empire as a process deeply embedded in the complicated system of maritime relations in East Asia during the pivotal second half of the nineteenth century.

Jean Piaget has spent a major part of his life work showing how thought is fundamentally derived from action. In Success and Understanding, this master psychologist inverts the question for the first time and considers how action is controlled by thought.
In a series of ingenious experiments, children are presented with physical puzzles just difficult enough to challenge their emerging skills. Under these conditions, Piaget reveals how the child comes to use his developing conceptual system to design strategies that result in successful actions. According to Piaget, it takes time for thought and action to enter into their familiar partnership. The young child has trouble using his ideas to guide his actions and must pass through several interesting stages before he can routinely coordinate idea and act.
Success and Understanding completes the Piagetian scheme for relating thought to action that was so brilliantly initiated in The Grasp of Consciousness (Harvard, 1976). Together, the two books form a major episode in the history of Piaget's remarkable career.


"Gene sharing" means that the different functions of a protein may share the same gene--that is, a protein produced by a gene evolved to fulfill a specialized function for one biological role may also perform alternate functions for other biological roles.
In the 1980s and early 1990s, Joram Piatigorsky and colleagues coined the term "gene sharing" to describe the use of multifunctional proteins as crystallins in the eye lens. In Gene Sharing and Evolution Piatigorsky explores the generality and implications of gene sharing throughout evolution and argues that most if not all proteins perform a variety of functions in the same and in different species, and that this is a fundamental necessity for evolution.
How is a gene identified, by its structure or its function? Do the boundaries of a gene include its regulatory elements? What is the influence of gene expression on natural selection of protein functions, and how is variation in gene expression selected in evolution? These are neither new nor resolved questions. Piatigorsky shows us that the extensiveness of gene sharing and protein multifunctionality offers a way of responding to these questions that sheds light on the complex interrelationships among genes, proteins, and evolution.


“How could I allow my soldiers to sail on this disloyal and cruel sea?” These words, attributed to the most powerful caliph of medieval Islam, Umar Ibn al-Khattab (634–644), have led to a misunderstanding in the West about the importance of the Mediterranean to early Islam. This body of water, known in Late Antiquity as the Sea of the Romans, was critical to establishing the kingdom of the caliphs and for introducing the new religion to Europe and Africa. Over time, it also became a pathway to commercial and political dominion, indispensable to the prosperity and influence of the Islamic world. Sea of the Caliphs returns Muslim sailors to their place of prominence in the history of the Islamic caliphate.
As early as the seventh century, Muslim sailors competed with Greek and Latin seamen for control of this far-flung route of passage. Christophe Picard recreates these adventures as they were communicated to admiring Muslims by their rulers. After the Arab conquest of southern Europe and North Africa, Muslims began to speak of the Mediterranean in their strategic visions, business practices, and notions of nature and the state. Jurists and ideologues conceived of the sea as a conduit for jihad, even as Muslims’ maritime trade with Latin, Byzantine, and Berber societies increased.
In the thirteenth century, Christian powers took over Mediterranean trade routes, but by that time a Muslim identity that operated both within and in opposition to Europe had been shaped by encounters across the sea of the caliphs.

In seventeenth-century England, intellectuals of all kinds discovered their idealized self-image in the Adam who investigated, named, and commanded the creatures. Reinvented as the agent of innocent curiosity, Adam was central to the project of redefining contemplation as a productive and public labor. It was by identifying with creation’s original sovereign, Joanna Picciotto argues, that early modern scientists, poets, and pamphleteers claimed authority as both workers and “public persons.”
Tracking an ethos of imitatio Adami across a wide range of disciplines and devotions, Picciotto reveals how practical efforts to restore paradise generated the modern concept of objectivity and a novel understanding of the author as an agent of estranged perception. Finally, she shows how the effort to restore Adam as a working collective transformed the corpus mysticum into a public. Offering new readings of key texts by writers such as Robert Hooke, John Locke, Andrew Marvell, Joseph Addison, and most of all John Milton, Labors of Innocence in Early Modern England advances a new account of the relationship between Protestantism, experimental science, the public sphere, and intellectual labor itself.


Valerian Pidmohylnyi’s The City was a landmark event in the history of Ukrainian literature. Written by a master craftsman in full control of the texture, rhythm, and tone of the text, the novel tells the story of Stepan, a young man from the provinces who moves to the capital of Ukraine, Kyiv, and achieves success as a writer through a succession of romantic encounters with women.
At its core, the novel is a philosophical search for harmony in a world where our intellectual side expects rational order, whereas the instinctive natural world follows its own principles. The resulting alienation and disorientation reflect the basic principles of existential philosophy, in which Pidmohylnyi is close to his European counterparts of the day.

A millennium ago, Baghdad was the capital of one of history’s greatest civilizations. A new Islamic era was under way. Yet despite the profound cultural achievements, many Muslims felt their society had gone astray. Shiˀa Muslims challenged the dominant narrative of Islamic success with stories of loss. Faithful Muslims have long debated whether Sunni caliphs or Shiˀa imams were the true heirs of the Prophet Muhammad. More influential has been the way Muslim communities remembered those disputes through stories that influenced how to think and feel about them, Matthew Pierce argues.
Twelve Infallible Men focuses on the role of narratives of the imams in the development of a distinct Shiˀa identity. During the tenth century, at a critical juncture in Islamic history, a group of scholars began assembling definitive works containing accounts of the twelve imams’ lives. These collective biographies constructed a sacred history, portraying the imams as strong, beautiful, learned, and pious. Miracles surrounded their birth, and they became miracle workers in turn, but were nevertheless betrayed and martyred by enemies.
These biographies inspired and entertained, but more importantly they offered a meaningful narrative of history for Muslims who revered the imams. The accounts invoked shared memories and shaped communal responses and ritual practices of grieving. Mourning the imams’ tragic fates helped nascent Shiˀa communities resist the pressure to forget their story. The biographies of the imams became a focal point of cultural memory, inspiring Shiˀa religious imagination for centuries to come.
READERS
Browse our collection.
PUBLISHERS
See BiblioVault's publisher services.
STUDENT SERVICES
Files for college accessibility offices.
UChicago Accessibility Resources
home | accessibility | search | about | contact us
BiblioVault ® 2001 - 2024
The University of Chicago Press









