298 start with M start with M

The authors provide a concise yet thorough introduction to the economic theory of environmental policy and natural resource management. They begin with an overview of environmental economics before exploring topics including cost-benefit analysis, market failures and successes, and economic growth and sustainability. Readers of the first edition will notice new analysis of cost estimation as well as specific market instruments, including municipal water pricing and waste disposal. Particular attention is paid to behavioral economics and cap-and-trade programs for carbon.
Throughout, Markets and the Environment is written in an accessible, student-friendly style. It includes study questions for each chapter, as well as clear figures and relatable text boxes. The authors have long understood the need for a book to bridge the gap between short articles on environmental economics and tomes filled with complex algebra. Markets and the Environment makes clear how economics influences policy, the world around us, and our own lives.


Today von Braun is recognized as the person most responsible for laying the groundwork for public acceptance of America's space program. When President Bush directed NASA in 1989 to prepare plans for an orbiting space station, lunar research bases, and human exploration of Mars, he was largely echoing what von Braun proposed in The Mars Project.

Mars enthusiasts will appreciate these perfect snapshots of our current understanding of Mars, with soon-to-be classic pictures that have come to define our vision of the Red Planet. These images and their interpretations will be held as a yardstick for future exploration as we learn more about the surface and geologic processes of the fourth planet from the Sun.
With tantalizing and artistic glimpses at actively eroding slopes, impact craters, strange polar landscapes, avalanches, and even spectacular descent pictures of probes like the Phoenix Lander and the Mars Science Laboratory, we see what researchers are seeing.
Through vivid and beautiful images, this book underscores the need for such a camera on future orbiters, especially as more landing missions are planned. Mars: The Pristine Beauty of the Red Planet provides a stunning keepsake of one of humanity’s greatest accomplishments in space travel.

This book explores both the human and natural history of the marshes between Toledo and Port Clinton, Ohio. The author, Louis Campbell is the acknowledged authority on the birds of the Toledo area. Mr. Campbell began weekly birding trips to the marshes in the 1920’s, carefully recording his observations. His discerning eye and inquiring mind have accumulated a wealth of information, presented here in a style that is comfortably conversational, whether the subject is glacial moraines, nesting eagles, or a drunken meadow mouse.
The book begins with an almanac, a celebration of marsh life throughout the year, enriched by personal experiences. Mr. Campbell’s encounters include a pair of bloodthirsty shrews, a roguish gallery of courting waterfowl, and a rhythm-challenged bittern. He invites the reader to share the risky pleasures of punting and the eerie night sounds of the marsh in May.
Part II describes the history of the low-lying marshes from the Ice Age to the present, as they were transformed into drained, flood-plagued farmland then to drought-and flood-plagued private hunting clubs, and finally to government-protected marshes sealed off by huge dikes from the gift and the threat of Lake Erie. Readers of this book will never again take these wetlands for granted.

Much like Vladimir Lenin, his onetime rival for the leadership of the Bolshevik party during its formative years, Alexander Bogdanov (1873–1928) was a visionary. In two science fiction novels set on Mars, Bogdanov imagined a future in which the workers of the world, liberated from capitalist exploitation, create a “physiological collective” that rejuvenates and unites its members through regular blood exchanges. But Bogdanov was not merely a dreamer. He worked tirelessly to popularize and realize his vision, founding the first research institute devoted to the science of blood transfusion.
In A Martian Stranded on Earth, the first broad-based book on Bogdanov in English, Nikolai Krementsov examines Bogdanov’s roles as revolutionary, novelist, and scientist, presenting his protagonist as a coherent thinker who pursued his ideas in a wide range of venues. Through the lens of Bogdanov’s involvement with blood studies on one hand, and of his fictional and philosophical writings on the other, Krementsov offers a nuanced analysis of the interactions between scientific ideas and societal values.
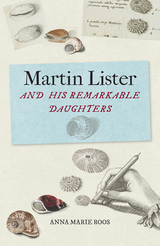
Susanna and Anna portrayed the shells of this collection not only as curious and beautiful objects, but also as specimens of natural history, rendering them with sensitivity and keen scientific empiricism. Beautiful in their own right, their illustrations and engravings reveal the early techniques behind scientific illustration and offer fascinating insight into the often hidden role of women in the scientific revolution.

In Masking Inequality with Good Intentions, Heather M. Falconer examines the impact of systemic bias on disciplinary discourse acquisition and identity development by asking “How do the norms and expectations of higher education and STEM, specifically, impact the development of scientific identity and discursive skill?” and “What role do societal markers like race and gender play in the negotiation of identity in STEM learning environments?”
Drawing on the experiences and writings of six students from historically underrepresented backgrounds in STEM, each participating in an undergraduate research program, Falconer discusses how programmatic and pedagogical choices can work to either further marginalize students and disrupt their writing and identity development as scientists or create counterspaces—spaces where students can thrive and push back against dominant, oppressive forces. Practical applications for pedagogy, curriculum, and program design are included.



In answering these questions, D. Graham Burnett brings to light the work of several such explorers, particularly Sir Robert H. Schomburgk, the man who claimed to be the first to reach the site of Ralegh's El Dorado. Commissioned by the Royal Geographical Society and later by the British Crown, Schomburgk explored and mapped regions in modern Brazil, Venezuela, and Guyana, always in close contact with Amerindian communities. Drawing heavily on the maps, reports, and letters that Schomburgk sent back to England, and especially on the luxuriant images of survey landmarks in his Twelve Views in the Interior of Guiana (reproduced in color in this book), Burnett shows how a vast network of traverse surveys, illustrations, and travel narratives not only laid out the official boundaries of British Guiana but also marked out a symbolic landscape that fired the British imperial imagination.
Engagingly written and beautifully illustrated, Masters of All They Surveyed will interest anyone who wants to understand the histories of colonialism and science.

When Isaac Newton published the Principia three centuries ago, only a few scholars were capable of understanding his conceptually demanding work. Yet this esoteric knowledge quickly became accessible in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries when Britain produced many leading mathematical physicists. In this book, Andrew Warwick shows how the education of these "masters of theory" led them to transform our understanding of everything from the flight of a boomerang to the structure of the universe.
Warwick focuses on Cambridge University, where many of the best physicists trained. He begins by tracing the dramatic changes in undergraduate education there since the eighteenth century, especially the gradual emergence of the private tutor as the most important teacher of mathematics. Next he explores the material culture of mathematics instruction, showing how the humble pen and paper so crucial to this study transformed everything from classroom teaching to final examinations. Balancing their intense intellectual work with strenuous physical exercise, the students themselves—known as the "Wranglers"—helped foster the competitive spirit that drove them in the classroom and informed the Victorian ideal of a manly student. Finally, by investigating several historical "cases," such as the reception of Albert Einstein's special and general theories of relativity, Warwick shows how the production, transmission, and reception of new knowledge was profoundly shaped by the skills taught to Cambridge undergraduates.
Drawing on a wealth of new archival evidence and illustrations, Masters of Theory examines the origins of a cultural tradition within which the complex world of theoretical physics was made commonplace.

In Masters of Uncertainty, Phaedra Daipha develops a new conceptual framework for the process of decision making, after spending years immersed in the life of a northeastern office of the National Weather Service. Arguing that predicting the weather will always be more craft than science, Daipha shows how forecasters have made a virtue of the unpredictability of the weather. Impressive data infrastructures and powerful computer models are still only a substitute for the real thing outside, and so forecasters also enlist improvisational collage techniques and an omnivorous appetite for information to create a locally meaningful forecast on their computer screens. Intent on capturing decision making in action, Daipha takes the reader through engrossing firsthand accounts of several forecasting episodes (hits and misses) and offers a rare fly-on-the-wall insight into the process and challenges of producing meteorological predictions come rain or come shine. Combining rich detail with lucid argument, Masters of Uncertainty advances a theory of decision making that foregrounds the pragmatic and situated nature of expert cognition and casts into new light how we make decisions in the digital age.

It is often assumed that natural philosophy was the forerunner of early modern natural sciences. But where did these sciences’ systematic observation and experimentation get their starts? In Materials and Expertise in Early Modern Europe, the laboratories, workshops, and marketplaces emerge as arenas where hands-on experience united with higher learning. In an age when chemistry, mineralogy, geology, and botany intersected with mining, metallurgy, pharmacy, and gardening, materials were objects that crossed disciplines.
Here, the contributors tell the stories of metals, clay, gunpowder, pigments, and foods, and thereby demonstrate the innovative practices of technical experts, the development of the consumer market, and the formation of the observational and experimental sciences in the early modern period. Materials and Expertise in Early Modern Europe showcases a broad variety of forms of knowledge, from ineffable bodily skills and technical competence to articulated know-how and connoisseurship, from methods of measuring, data gathering, and classification to analytical and theoretical knowledge. By exploring the hybrid expertise involved in the making, consumption, and promotion of various materials, and the fluid boundaries they traversed, the book offers an original perspective on important issues in the history of science, medicine, and technology.

Phrenology was the most popular mental science of the Victorian age. From American senators to Indian social reformers, this new mental science found supporters around the globe. Materials of the Mind tells the story of how phrenology changed the world—and how the world changed phrenology.
This is a story of skulls from the Arctic, plaster casts from Haiti, books from Bengal, and letters from the Pacific. Drawing on far-flung museum and archival collections, and addressing sources in six different languages, Materials of the Mind is an impressively innovative account of science in the nineteenth century as part of global history. It shows how the circulation of material culture underpinned the emergence of a new materialist philosophy of the mind, while also demonstrating how a global approach to history can help us reassess issues such as race, technology, and politics today.

Evolutionary maternal effects occur whenever a mother’s phenotypic traits directly affect her offspring’s phenotype, independent of the offspring’s genotype. Some of the phenotypic traits that result in maternal effects have a genetic basis, whereas others are environmentally determined. For example, the size of a litter produced by a mammalian mother—a trait with a strong genetic basis—can affect the growth rate of her offspring, while a mother’s dominance rank—an environmentally determined trait—can affect the dominance rank of her offspring.
The first volume published on the subject in more than a decade, Maternal Effects in Mammals reflects advances in genomic, ecological, and behavioral research, as well new understandings of the evolutionary interplay between mothers and their offspring. Dario Maestripieri and Jill M. Mateo bring together a learned group of contributors to synthesize the vast literature on a range of species, highlight evolutionary processes that were previously overlooked, and propose new avenues of research. Maternal Effects in Mammals will serve as the most comprehensive compendium on and stimulus for interdisciplinary treatments of mammalian maternal effects.

The idea that a woman may leave a biological trace on her gestating offspring has long been a commonplace folk intuition and a matter of scientific intrigue, but the form of that idea has changed dramatically over time. Beginning with the advent of modern genetics at the turn of the twentieth century, biomedical scientists dismissed any notion that a mother—except in cases of extreme deprivation or injury—could alter her offspring’s traits. Consensus asserted that a child’s fate was set by a combination of its genes and post-birth upbringing.
Over the last fifty years, however, this consensus was dismantled, and today, research on the intrauterine environment and its effects on the fetus is emerging as a robust program of study in medicine, public health, psychology, evolutionary biology, and genomics. Collectively, these sciences argue that a woman’s experiences, behaviors, and physiology can have life-altering effects on offspring development.
Tracing a genealogy of ideas about heredity and maternal-fetal effects, this book offers a critical analysis of conceptual and ethical issues—in particular, the staggering implications for maternal well-being and reproductive autonomy—provoked by the striking rise of epigenetics and fetal origins science in postgenomic biology today.

Over the last several decades, mathematical models have become central to the study of social evolution, both in biology and the social sciences. But students in these disciplines often seriously lack the tools to understand them. A primer on behavioral modeling that includes both mathematics and evolutionary theory, Mathematical Models of Social Evolution aims to make the student and professional researcher in biology and the social sciences fully conversant in the language of the field.
Teaching biological concepts from which models can be developed, Richard McElreath and Robert Boyd introduce readers to many of the typical mathematical tools that are used to analyze evolutionary models and end each chapter with a set of problems that draw upon these techniques. Mathematical Models of Social Evolution equips behaviorists and evolutionary biologists with the mathematical knowledge to truly understand the models on which their research depends. Ultimately, McElreath and Boyd’s goal is to impart the fundamental concepts that underlie modern biological understandings of the evolution of behavior so that readers will be able to more fully appreciate journal articles and scientific literature, and start building models of their own.




Mathematics and Religion: Our Languages of Sign and Symbol is the sixth title published in the Templeton Science and Religion Series, in which scientists from a wide range of fields distill their experience and knowledge into brief tours of their respective specialties. In this volume, Javier Leach, a mathematician and Jesuit priest, leads a fascinating study of the historical development of mathematical language and its influence on the evolution of metaphysical and theological languages.
Leach traces three historical moments of change in this evolution: the introduction of the deductive method in Greece, the use of mathematics as a language of science in modern times, and the formalization of mathematical languages in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As he unfolds this fascinating history, Leach notes the striking differences and interrelations between the two languages of science and religion. Until now there has been little reflection on these similarities and differences, or about how both languages can complement and enrich each other.

In a substantive introductory essay, the editors explain the notion of "postclassical theory" and discuss the significance of ideas such as emergence and undecidability in current work in and on science and mathematics. Other essays include a witty examination of the relations among mathematical thinking, writing, and the technologies of virtual reality; an essay that reconstructs the conceptual practices that led to a crucial mathematical discovery—or construction—in the 19th century; a discussion of the implications of Bohr’s complementarity principle for classical ideas of reality; an examination of scientific laboratories as "hybrid" communities of humans and nonhumans; an analysis of metaphors of control, purpose, and necessity in contemporary biology; an exploration of truth and lies, and the play of words and numbers in Shakespeare, Frege, Wittgenstein, and Beckett; and a final chapter on recent engagements, or nonengagements, between rationalist/realist philosophy of science and contemporary science studies.
Contributors. Malcolm Ashmore, Michel Callon, Owen Flanagan, John Law, Susan Oyama, Andrew Pickering, Arkady Plotnitsky, Brian Rotman, Barbara Herrnstein Smith, John Vignaux Smyth, E. Roy Weintraub

Chemists, Morris shows, are one of the leading drivers of innovation in laboratory design and technology. He tells of fascinating lineages of invention and innovation, for instance, how the introduction of coal gas into Robert Wilhelm Bunsen’s laboratory led to the eponymous burner, which in turn led to the development of atomic spectroscopy. Comparing laboratories across eras, from the furnace-centered labs that survived until the late eighteenth century to the cleanrooms of today, he shows how the overlooked aspects of science—the architectural design and innovative tools that have facilitated its practice—have had a profound impact on what science has been able to do and, ultimately, what we have been able to understand.

Take a deep breath. Air—without it, life on Earth would cease to exist. Though not usually seen, its presence is relied upon. At once both ethereal and physical, air has been associated with flight and spirit, and yet it has progressively become a territory that can be claimed through communications, warfare, travel, and scientific exploration. At the same time, air is no longer a completely reliable part of our daily life: like water, it has become an environmental element that must be watched closely for quality and purity.
A Matter of Air investigates the meanings of air over the last three centuries, including our modern concern over emissions and climate change. Steven Connor looks at the human relationship with air, both positive and negative. His explorations include the dangers posed by radio atmospherics, poison gas, and haze as well as our continued fascination with effervescence and explosives. Drawing ideas from religion, science, art, literature, and philosophy, A Matter of Air creates a comprehensive history of the human perception of air. Thoroughly researched and written with wit and quirky enthusiasm, the book will appeal to a wide range of general readers interested in the environment, human history, and our most essential aspects of life.

Ajzenberg-Selove came to America at the age of 15 after narrowly escaping the Nazi takeover of France. She had planned to become an engineer like her father, but switched to physics after she was told the only engineering jobs open to women were in drafting: Marie Curie's example proved to her that women could do physics. Her first attempt at graduate work at Columbia University was a disaster, but she was sturck with the intellectual beauty of the field. After taking a Ph.D. in physics at University of Wisconsin, she did post-doctoral work with Thomas Lauritsen at the California Institute of Technology, where she began writing the first of a series of major review papers on the nuclear spectroscopy of the light nuclei, a subject of fundamental importance to nuclear physics, astrophysics, and applied physics. She continued this work and experimental research for thirty-eight years while teaching at Boston University, Haverford College, and the University of Pennsylvania.
During her early career, Ajzenberg-Selove was shielded by her male mentors from experiencing much of the discrimination directed against women in science. Her simultaneous battles to become a tenured professor and to overcome breast cancer opened her eyes and confirmed her as a feminist.
The lay reader and the scientist alike will be fascinated by Ajzenberg-Selove's clear portrayal of her interlinked lives as physicist, teacher, wife of particle physicist, Walter Selove, and a woman who relishes both competition and friendship in a male-dominated field. An invaluable book for anyone contemplating a career in science.


In A Matter of Life and Death, anthropologist Marc Boglioli puts a human face on a group widely regarded as morally suspect, one that currently stands in the crossfire of America's so-called culture wars. Drawing on extensive ethnographic fieldwork in Addison County, Vermont, which took him from hunting camps and sporting goods stores to local bars and kitchen tables, Boglioli focuses on how contemporary hunters, women as well as men, understand their relationship to their prey. He shows how hunters' attitudes toward animals flow directly from the rural lifeways they have continued to maintain in the face of encroaching urban sensibilities. The result is a rare glimpse into a culture that experiences wild animals in a way that is at once violent, consumptive, and respectful, and that regards hunting as an enduring link to a vanishing past. It is a book that will challenge readers—hunters, non-hunters, and anti-hunters alike—to reconsider what constitutes a morally appropriate relationship with the non-human residents of this planet.

To care can feel good, or it can feel bad. It can do good, it can oppress. But what is care? A moral obligation? A burden? A joy? Is it only human? In Matters of Care, María Puig de la Bellacasa presents a powerful challenge to conventional notions of care, exploring its significance as an ethical and political obligation for thinking in the more than human worlds of technoscience and naturecultures.
Matters of Care contests the view that care is something only humans do, and argues for extending to non-humans the consideration of agencies and communities that make the living web of care by considering how care circulates in the natural world. The first of the book’s two parts, “Knowledge Politics,” defines the motivations for expanding the ethico-political meanings of care, focusing on discussions in science and technology that engage with sociotechnical assemblages and objects as lively, politically charged “things.” The second part, “Speculative Ethics in Antiecological Times,” considers everyday ecologies of sustaining and perpetuating life for their potential to transform our entrenched relations to natural worlds as “resources.”
From the ethics and politics of care to experiential research on care to feminist science and technology studies, Matters of Care is a singular contribution to an emerging interdisciplinary debate that expands agency beyond the human to ask how our understandings of care must shift if we broaden the world.

This volume reproduces major portions of the text of Maxwell's classic papers on concepts that are key to both modern physics and the modern world. Through Simpson's engaginbg commentaries and notes and Anne Farrell's illustrations, readers with limited knowledge of math or physics as well as scientists and historians of science will be able to follow the emergence of Maxwell's ideas and to appreciate the magnitude of his achievement. This book includes a long biographical introduction that explores the personal, historical, and scientific context of Maxwell's book.

In Maxwell Street, Cresswell advocates approaching the study of place as an “assemblage” of things, meanings, and practices. He models this innovative approach through a montage format that exposes the different types of texts—primary, secondary, and photographic sources—that have attempted to capture the essence of the area. Cresswell studies his historical sources just as he explores the different elements of Maxwell Street—exposing them layer by layer. Brilliantly interweaving words and images, Maxwell Street sheds light on a historic Chicago neighborhood and offers a new model for how to write about place that will interest anyone in the fields of geography, urban studies, or cultural history.

This provocative new reading of Darwin goes directly to the origins of evolutionary theory. Unlike most contemporary biologists or historians and philosophers of science, Richards holds that Darwin did concern himself with the idea of progress, or telos, as he constructed his theory. Richards maintains that Darwin drew on the traditional embryological meanings of the terms "evolution" and "descent with modification." In the 1600s and 1700s, "evolution" referred to the embryological theory of preformation, the idea that the embryo exists as a miniature adult of its own species that simply grows, or evolves, during gestation. By the early 1800s, however, the idea of preformation had become the concept of evolutionary recapitulation, the idea that during its development an embryo passes through a series of stages, each the adult form of an ancestor species.
Richards demonstrates that, for Darwin, embryological recapitulation provided a graphic model of how species evolve. If an embryo could be seen as successively taking the structures and forms of its ancestral species, then one could see the evolution of life itself as a succession of species, each transformed from its ancestor. Richards works with the Origin and other published and archival material to show that these embryological models were much on Darwin's mind as he considered the evidence for descent with modification.
Why do so many modern researchers find these embryological roots of Darwin's theory so problematic? Richards argues that the current tendency to see evolution as a process that is not progressive and not teleological imposes perspectives on Darwin that incorrectly deny the clearly progressive heart of his embryological models and his evolutionary theory.

"Rudwick has not merely written the first book-length history of palaeontology in the English language; he has written a very intelligent one. . . . His accounts of sources are rounded and organic: he treats the structure of arguments as Cuvier handled fossil bones."—Roy S. Porter, History of Science

As smartphones mediate more of our activities, they are changing our relationship with meaning. To a teenager, for example a “conversation” is just as likely to refer to an exchange of text messages as it is a face-to-face discussion. Meanwhile, Facebook has redefined what friendship means, Snapchat what a memory means, etc. The kinds of changes smartphones bring are happening at rapid pace: TikTok reached a billion users in just over three years, whereas it took the telephone 75 years to reach a tenth of that number of people. Meaningful Technologies: How Digital Metaphors Change the Way We Think and Live by Eric Chown and Fernando Nascimento offers systematic reconsideration of the ways in which digital technologies impact our lives both individually and collectively.
Metaphors aren’t just a clever way to describe technology, they are also changing the way we think. When we click on a picture of a shopping cart it connects a complex set of technologies to represent a simple idea that we’re all familiar with. A heart icon under a photo is understood as an easy way to express appreciation. We aren’t required to understand how technology works, just how we interact with it. The ambiguity of metaphors, and the complexity of technology can also hide important realities about what is being described. “The cloud,” for example, actually consists of very real data centers, which consume huge amounts of natural resources to keep running. Meanwhile, pressing that heart icon on a photo is a signal to the artificial intelligences running in your app that you want to see more things like that photo and that it should adjust what it knows about you accordingly.
There is a constant feedback loop between us and the digital technologies we use. We are constantly using them and they are changing us through their usage. Meaningful Technologies focuses on this loop from the perspectives of hermeneutic philosophy and cognitive science. Through the former, the authors examine meaning and how it changes over time. Through the latter, they gain understanding of how this feedback loop impacts individuals, especially in terms of learning and attention. Chown and Nascimento argue that, on the one hand, apps have a kind of agency never before possible in a technology, but also that, armed with a critical framework for examining such apps, we can regain some of our own agency. This book will appeal to scholars of digital media digital and computational studies, and those interested in issues related to ethical impacts of digital technologies.

Westerners think of time as a measure of duration, a metric quantity that is continuous, homogeneous, unchangeable, and never ending—a reality that lies outside of human existence. How did the people of Mesoamerica and the Andes, isolated as they were from the rest of the world, conceive of their histories? How and why did they time their rituals? What knowledge can we acquire about their time from studying the material record they have left behind?
This volume brings together specialists in anthropology, archaeology, art history, astronomy, and the history of science to contemplate concrete and abstract temporal concepts gleaned from the Central Mexicans, Mayans, and Andeans. Contributors first address how people reckon and register time; they compare the western linear, progressive way of knowing time with the largely cyclic notions of temporality derived from the Americas, and they dissect, explain, and explore the origins of the complex dynastic and ritual calendars of the Maya, Inca, and Aztecs. They subsequently consider how people sense time and its moral dimensions. Time becomes an inescapable feature of the process of perception, an entity that occupies a succession of moments rather than the knife-edge present ingrained in our Western minds.


Pressures of population growth, rapid urbanization, industrialization, and stress on natural resources provide new challenges to the Asian Development Bank as it strives to set forth environmental issues as an important element of sustainable economic development in the Asian and Pacific region. While the Bank can provide policy and technical guidance, the governments themselves must take the lead in providing the resources and policies needed to address effectively the rapidly changing environmental condition. How we measure the effectiveness of governmental performance in meeting the environmental challenge in Asia and the Pacific is the subject of this book.
By drawing on experiences in six Asian and Pacific countries, the authors have developed a series of methodological tools to assist others in assessing the environmental quality of air, water, soil, and biological diversity in developing countries. These tools can then be used to determine the financial resources needed to achieve the quality of life characteristic of a sustainable development path.



The Fifth edition of this classic textbook includes a solutions manual. Extensive supplemental instructor resources are forthcoming in the Fall of 2022.
Mechanical Vibration: Theory and Application presents comprehensive coverage of the fundamental principles of mechanical vibration, including the theory of vibration, as well as discussions and examples of the applications of these principles to practical engineering problems. The book also addresses the effects of uncertainties in vibration analysis and design and develops passive and active methods for the control of vibration. Many example problems with solutions are provided. These examples as well as compelling case studies and stories of real-world applications of mechanical vibration have been carefully chosen and presented to help the reader gain a thorough understanding of the subject.There is a solutions manual for instructors who adopt this book. Request a solutions manual here (https://www.rutgersuniversitypress.org/mechanical-vibration).


We often think of reason as a fixed entity, as a definitive body of facts that do not change over time. But during the Enlightenment, reason also was seen as a process, as a set of skills enacted on a daily basis. How, why, and where were these skills learned? Concentrating on Scottish students living during the long eighteenth century, this book argues that notebooks were paper machines and that notekeeping was a capability-building exercise that enabled young notekeepers to mobilize everyday handwritten and printed forms of material and visual media in a way that empowered them to judge and enact the enlightened principles they encountered in the classroom. Covering a rich selection of material ranging from simple scribbles to intricate watercolor diagrams, the book reinterprets John Locke’s comparison of the mind to a blank piece of paper, the tabula rasa. Although one of the most recognizable metaphors of the British Enlightenment, scholars seldom consider why it was so successful for those who used it. Each chapter uses one core notekeeping skill to reveal the fascinating world of material culture that enabled students in the arts, sciences, and humanities to transform the tabula rasa metaphor into a dynamic cognitive model. Starting in the home, moving to schools, and ending with universities, the book reconstructs the relationship between media and the mind from the bottom up. It reveals that the cognitive skills required to make and use notebooks were not simply aids to reason; rather, they were part of reason itself.


Award-winning author David J. Park argues that the battle against global warming is also a fight for media reform. With his new book Media Reform and the Climate Emergency: Rethinking Communication in the Struggle for a Sustainable Future, he critically examines how advertising, the digital infrastructure, and journalism advance the climate emergency and lays out a path of reform to help create a more sustainable world. The production and consumption of goods and services within consumer societies lead to unsustainable greenhouse gas emissions, and Park finds that much of mass communication is either dependent upon or closely tied to the success of this social organization. As a result, he suggests successful environmental movements creatively dismantle or reform institutional infrastructures that extend the planetary global warming crisis and the unsustainable consumption of nature.
Communication policies and industries are part of these infrastructures. Advertising evolved to propel a new consumer society that would encourage the over-consumption of goods and services with harmful and unsustainable production processes. Our digital infrastructure is largely premised upon the surveillance of online consumer habits and preferences, with the goal to create individualized messages to more effectively persuade people to increase their consumption habits. Much of commercial journalism resists the drastic and immediate regulatory changes necessary to address the worst aspects of this crisis. This is because so many of the needed changes challenge the media’s source of income, their libertarian philosophy, and the general status quo, which is preferred by elites. Bound to foster conversations among scholars, activists, politicians, and those who work in the communication industries, this book rethinks mass communication and highlights how immediate reform is needed in the struggle for a sustainable planet.

Drawing on a wealth of previously unused archival material, Medical Monopoly combines legal, medical, and business history to offer a sweeping new interpretation of the origins of the complex and often troubling relationship between the pharmaceutical industry and medical practice today. Joseph M. Gabriel provides the first detailed history of patent and trademark law as it relates to the nineteenth-century pharmaceutical industry as well as a unique interpretation of medical ethics, therapeutic reform, and the efforts to regulate the market in pharmaceuticals before World War I. His book will be of interest not only to historians of medicine and science and intellectual property scholars but also to anyone following contemporary debates about the pharmaceutical industry, the patenting of scientific discoveries, and the role of advertising in the marketplace.

A personal account of the aging body and advanced technologies by a preeminent philosopher of technology
Medical Technics is a rigorous examination of how medical progress has modified our worlds and contributed to a virtual revolution in longevity. Don Ihde offers a unique autobiographical tour of medical events experienced in a decade, beginning in his 70s. Ihde offers experiential and postphenomenological analyses of technologies such as sonography and microsurgery, and ultimately asks what it means to increasingly become a cyborg.
Forerunners: Ideas FirstShort books of thought-in-process scholarship, where intense analysis, questioning, and speculation take the lead


The first comprehensive edition and translation of Old English writings on health and healing in more than 150 years.
Unlike elsewhere in Europe, vernacular writings on health and healing had a major place in early medieval England. These texts—unique local remedies and translations of late antique Latin treatises—offer insights into the history of science and medicine, social history, scribal practices, and culture. Some cures resemble ones still used today; others are linguistically extravagant, prescribing ambitious healing practices. Alongside recipes for everyday ailments such as headaches are unparalleled procedures for preventing infant mortality, restoring lost cattle, warding off elf-shot, or remedying the effects of flying venom.
Medical Writings from Early Medieval England presents the first comprehensive edition and translation from Old English of these works in more than 150 years. Volume I includes The Old English Herbal, Remedies from Animals, Lacnunga, the Peri Didaxeon, and a compendium of miscellaneous texts.

In his time, Head was best known for his research into the human nervous system. He did a series of experiments in collaboration with W. H. R. Rivers in which cutaneous nerves were surgically severed in Head's arm and the stages by which sensation returned were chartered over several years. Head’s friend, the philosopher Alfred North Whitehead, drew out the epistemological implications of how, in this new conception, the nervous system furthered the knowledge of the world.

The colonial encounter between France and Morocco took place not only in the political realm but also in the realm of medicine. Because the body politic and the physical body are intimately linked, French efforts to colonize Morocco took place in and through the body. Starting from this original premise, Medicine and the Saints traces a history of colonial embodiment in Morocco through a series of medical encounters between the Islamic sultanate of Morocco and the Republic of France from 1877 to 1956.
Drawing on a wealth of primary sources in both French and Arabic, Ellen Amster investigates the positivist ambitions of French colonial doctors, sociologists, philologists, and historians; the social history of the encounters and transformations occasioned by French medical interventions; and the ways in which Moroccan nationalists ultimately appropriated a French model of modernity to invent the independent nation-state. Each chapter of the book addresses a different problem in the history of medicine: international espionage and a doctor’s murder; disease and revolt in Moroccan cities; a battle for authority between doctors and Muslim midwives; and the search for national identity in the welfare state. This research reveals how Moroccans ingested and digested French science and used it to create a nationalist movement and Islamist politics, and to understand disease and health. In the colonial encounter, the Muslim body became a seat of subjectivity, the place from which individuals contested and redefined the political.


Pinto focuses on the distinct tradition of maps known collectively as the Book of Roads and Kingdoms (Kitab al-Masalik wa al-Mamalik, or KMMS), examining them from three distinct angles—iconography, context, and patronage. She untangles the history of the KMMS maps, traces their inception and evolution, and analyzes them to reveal the identities of their creators, painters, and patrons, as well as the vivid realities of the social and physical world they depicted. In doing so, Pinto develops innovative techniques for approaching the visual record of Islamic history, explores how medieval Muslims perceived themselves and their world, and brings Middle Eastern maps into the forefront of the study of the history of cartography.


In an agential realist account, the world is made of entanglements of “social” and “natural” agencies, where the distinction between the two emerges out of specific intra-actions. Intra-activity is an inexhaustible dynamism that configures and reconfigures relations of space-time-matter. In explaining intra-activity, Barad reveals questions about how nature and culture interact and change over time to be fundamentally misguided. And she reframes understanding of the nature of scientific and political practices and their “interrelationship.” Thus she pays particular attention to the responsible practice of science, and she emphasizes changes in the understanding of political practices, critically reworking Judith Butler’s influential theory of performativity. Finally, Barad uses agential realism to produce a new interpretation of quantum physics, demonstrating that agential realism is more than a means of reflecting on science; it can be used to actually do science.

A whirlwind journey through fungus frontiers that underscores how appreciating fungi is key to understanding our planet’s power and fragility.
What can we learn from the lives of fungi? Splitting time between the northern and southern hemispheres, ecologist Alison Pouliot ensures that she experiences two autumns per year in the pursuit of fungi—from Australia’s deserts to Iceland’s glaciers to America’s Cascade Mountains. In Meetings with Remarkable Mushrooms, we journey alongside Pouliot, magnifiers in hand, as she travels the world.
With Pouliot as our guide, we smell fire-loving truffles that transform their scent after burning to lure mammals who eat them and, ultimately, spread their spores. We spot the eerie glow of the ghost fungus, a deceptive entity that looks like an edible oyster mushroom but will soon heave back out—along with everything else in your stomach—if you take a bite. And we crawl alongside vegetable caterpillars, which are neither vegetable nor caterpillar but a fungus that devours insects from the inside out.
Featuring stunning color photographs of these mycological miracles, Meetings with Remarkable Mushrooms shows that understanding fungi is fundamental for harmonizing with the natural world.

Membranes to Molecular Machines explores just how late twentieth-century science came to think of our cells and bodies this way. This story is told through the lens of membrane research, an unwritten history at the crossroads of molecular biology, biochemistry, physiology, and the neurosciences, that directly feeds into today's synthetic biology as well as nano- and biotechnology. Mathias Grote shows how these sciences not only have made us think differently about life, they have, by reworking what membranes and proteins represent in laboratories, allowed us to manipulate life as "active matter" in new ways. Covering the science of biological membranes in the United States and Europe from the mid-1960s to the 1990s, this book connects that history to contemporary work with optogenetics, a method for stimulating individual neurons using light, and will enlighten and provoke anyone interested in the intersection of chemical research and the life sciences—from practitioner to historian to philosopher.
The research described in the book and its central actor, Dieter Oesterhelt, were honored with the 2021 Albert Lasker Basic Medical Research Award for his contribution to the development of optogenetics.

Picture your twenty-first birthday. Did you have a party? If so, do you remember who was there? Now step back: how clear are those memories? Should we trust them to be accurate, or is there a chance that you’re remembering incorrectly? And where have the many details you can no longer recall gone? Are they hidden somewhere in your brain, or are they gone forever?
Such questions have fascinated scientists for hundreds of years, and, as Alison Winter shows in Memory: Fragments of a Modern History, the answers have changed dramatically in just the past century. Tracing the cultural and scientific history of our understanding of memory, Winter explores early metaphors that likened memory to a filing cabinet; later, she shows, that cabinet was replaced by the image of a reel of film, ever available for playback. That model, too, was eventually superseded, replaced by the current understanding of memory as the result of an extremely complicated, brain-wide web of cells and systems that together assemble our pasts. Winter introduces us to innovative scientists and sensationalistic seekers, and, drawing on evidence ranging from scientific papers to diaries to movies, explores the way that new understandings from the laboratory have seeped out into psychiatrists' offices, courtrooms, and the culture at large. Along the way, she investigates the sensational battles over the validity of repressed memories that raged through the 1980s and shows us how changes in technology—such as the emergence of recording devices and computers—have again and again altered the way we conceptualize, and even try to study, the ways we remember.
Packed with fascinating details and curious episodes from the convoluted history of memory science, Memory is a book you'll remember long after you close its cover.


Males account for roughly 50 percent of the global population, but in America and other places, they account for over 85 percent of violent crime. A graph of relative risk of death in human males shows that mortality is high immediately following birth, falls during childhood, then exhibits a distinct rise between the ages of 15 and 35—primarily the result of accidents, violence, and risky behaviors. Why? What compels males to drive fast, act violently, and behave stupidly? Why are men's lives so different from those of women?
Men presents a new approach to understanding the human male by drawing upon life history and evolutionary theory. Because life history theory focuses on the timing of, and energetic investment in, particular aspects of physiology, such as growth and reproduction, Richard Bribiescas and his fellow anthropologists are now using it in the study of humans. This has led to an increased understanding of human female physiology—especially growth and reproduction—from an evolutionary and life history perspective. However, little attention has been directed toward these characteristics in males. Men provides a new understanding of human male physiology and applies it to contemporary health issues such as prostate cancer, testosterone replacement therapy, and the development of a male contraceptive.
Men proves that understanding human physiology requires global research in traditionally overlooked areas and that evolutionary and life history theory have much to offer toward this endeavor.


The Mental and the Physical was first published in 1967. Minnesota Archive Editions uses digital technology to make long-unavailable books once again accessible, and are published unaltered from the original University of Minnesota Press editions.
Professor Feigl's essay "The 'Mental' and the 'Physical'" has provoked a great deal of comment, criticism, and discussion since it first appeared as a part of the content of Volume II of the Minnesota Studies in the Philosophy of Science about ten years ago. Now Professor Feigl takes account of the critical discussions and presents his own comments with respect to the most important points raised in the criticisms. The essay itself is presented here in full, along with the postscript. The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science has called the essay "a 'super-colossal' survey of the mind-body problem." In its review of the earlier book containing the essay, Thought said: "This essay deserves careful reading by every philosopher concerned with genuine philosophical dialogue."

Mentality and Machines was first published in 1985. Minnesota Archive Editions uses digital technology to make long-unavailable books once again accessible, and are published unaltered from the original University of Minnesota Press editions.
Mentality and Machines — with a new preface and an extended postscript—is a general essay on the philosophy of mind, oriented to philosophical and psychological questions about real as well as imagined, robots and machines. The second edition retains all of the essays from the original book, including Gunderson's influential critique ("The Imitation Game") of A.M. Turing's treatment of the question "Can machines think?" and his controversial distinction between program-receptive and program-resistant aspects of the mind. This edition's postscript includes further reflections on these themes and others, and relates them to recent writings of other philosophers and computer scientists.

In Merchants of Medicines, Zachary Dorner follows the earliest industrial pharmaceuticals from their manufacture in the United Kingdom, across trade routes, and to the edges of empire, telling a story of what medicines were, what they did, and what they meant. He brings to life business, medical, and government records to evoke a vibrant early modern world of London laboratories, Caribbean estates, South Asian factories, New England timber camps, and ships at sea. In these settings, medicines were produced, distributed, and consumed in new ways to help confront challenges of distance, labor, and authority in colonial territories. Merchants of Medicines offers a new history of economic and medical development across early America, Britain, and South Asia, revealing the unsettlingly close ties among medicine, finance, warfare, and slavery that changed people’s expectations of their health and their bodies.

In this fully up-to-date and beautifully illustrated account, William Sheehan describes the growth of our knowledge of planet Mercury. From the puzzles it posed for early astronomers to radar studies in the 1960s, and from the first spacecraft fly-bys by the Mariner 10 probe in the 1970s to the latest images from the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging (MESSENGER) orbital mission between 2011 and 2015, Mercury has slowly been brought into clear focus. But although we have now mapped its surface in exquisite detail, revealing strange features like volcanic plains and water-ice deposits in craters near the poles, mysteries remain—such as why its core has the highest iron content of any body of the Solar System. Rather than growing duller on closer acquaintance, this most mercurial of planets continues to fascinate us, offering important clues to scientists as they seek to better understand the origin and evolution of the Earth.

"This book is another in the excellent University of Arizona Space Science Series, each of which is based on a conference. . . .but goes far beyond a conference proceedings to present a comprehensive summary of current knowledge. . . .I recommend this book as a valuable compendium of current knowledge."—Pageoph
"This collection will be a most valuable addition to any research library."—Choice

Even after 150 years, Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection is irresistibly compelling. But how can this idea—in which competition prevails—be consistent with all that we know about the thoroughly cooperative nature of life at the genetic and cellular level? This book reconciles these discrepancies.
Assembling a set of general principles, authors Kenneth Weiss and Anne Buchanan build a comprehensive, unified theory that applies on the evolutionary time scale but also on the developmental and ecological scales where daily life is lived, and cells, organisms, and species interact. They present this story through a diversity of examples spanning the fundamental challenges that organisms have faced throughout the history of life. This shows that even very complex traits can be constructed simply, based on these principles. Although relentless competitive natural selection is widely assumed to be the primary mover of evolutionary change, The Mermaid’s Tale shows how life more generally works on the basis of cooperation. The book reveals that the focus on competition and cooperation is largely an artifact of the compression of time—a distortion that dissolves when the nature and origins of adapted life are viewed primarily from developmental and evolutionary time scales.

Beginning each chapter on a particular island, Hanski dives into reflections on his own field studies before going on to pursue a variety of ecological questions, including: What is the biodiversity crisis? What are extinction thresholds and extinction debts? What can the biodiversity hypothesis tell us about rapidly increasing allergies, asthma, and other chronic inflammatory disorders? The world’s largest island, Greenland, for instance, is the starting point for a journey into the benefits that humankind acquires from biodiversity, including the staggering biodiversity of microbes in the ecosystems that are closest to us—the ecosystems in our guts, in our respiratory tracts, and under our skin. Conceptually oriented but grounded in an adventurous personal narrative, Messages from Islands is a landmark work that lifts the natural mysteries of islands from the sea, bringing to light the thrilling complexities and connections of ecosystems worldwide.

Drawing on ethnographic research in Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico, the contributors to Mestizo Genomics explore how the concepts of race, ethnicity, nation, and gender enter into and are affected by genomic research. In Latin America, national identities are often based on ideas about mestizaje (race mixture), rather than racial division. Since mestizaje is said to involve relations between European men and indigenous or African women, gender is a key factor in Latin American genomics and in the analyses in this book. Also important are links between contemporary genomics and recent moves toward official multiculturalism in Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico. One of the first studies of its kind, Mestizo Genomics sheds new light on the interrelations between "race," identity, and genomics in Latin America.
Contributors. Adriana Díaz del Castillo H., Roosbelinda Cárdenas, Vivette García Deister, Verlan Valle Gaspar Neto, Michael Kent, Carlos López Beltrán, María Fernanda Olarte Sierra, Eduardo Restrepo, Mariana Rios Sandoval, Ernesto Schwartz-Marín, Ricardo Ventura Santos, Peter Wade

Freshwater turtles and goldfish can survive for several days without oxygen, some diving turtles for several months; hibernating animals can exist without food for long periods; others can survive extreme conditions such as desiccation, freezing, and thawing. These creatures are, in effect, self-sustaining life-support systems, with a mysterious ability to regulate their own metabolisms.
These capabilities raise important questions, which Hochachka and Guppy explore in this seminal new book. What mechanisms turn down (or off) cell metabolism and other cell functions? How does an animal such as an opossum know when to activate mechanisms for slowing or stopping tissue and organ functions? How does it know when to turn them on again? How extensive is metabolic arrest as a defense against harsh environmental conditions? Can we decipher universal principles of metabolic arrest from available data? The lessons to be learned are of potentially great interest to clinicians, because the authors provide a theoretical framework in which to organize an attack on the all-too-practical problem of protecting tissues against hypoxia. Areas that may be influenced include research on cardiac arrest, strokes, acute renal failure, liver ischemia, lung injury, respiratory defense syndrome, claudication, shock, and organ transplant. Investigation of other metabolic arrest mechanisms may be similarly useful in both clinical and agricultural fields.
This is a pioneering book of great use to biomedical/clinical researchers and to biologists, biochemists, and physiologists generally.

An engaging critique of the science and metaphysics behind our understanding of the universe
The James Webb Space Telescope, when launched in 2021, will be the premier orbital observatory, capable of studying every phase of the history of the universe, from the afterglow of the Big Bang to the formation of our solar system. Examining the theoretical basis for key experiments that have made this latest venture in astrophysics possible, Bjørn Ekeberg reveals that scientific cosmology actually operates in a twilight zone between the physical and metaphysical.
Metaphysical Experiments explains how our current framework for understanding the universe, the Big Bang theory, is more determined by a deep faith in mathematical universality than empirical observation. Ekeberg draws on philosophical insights by Spinoza, Bergson, Heidegger, and Arendt; on the critical perspectives of Latour, Stengers, and Serres; and on cutting-edge physics research at the Large Hadron Collider, to show how the universe of modern physics was invented to reconcile a Christian metaphysical premise with a claim to the theoretical unification of nature.
By focusing on the nonmathematical assumptions underlying some of the most significant events in modern science, Metaphysical Experiments offers a critical history of contemporary physics that demystifies such concepts as the universe, particles, singularity, gravity, blackbody radiation, the speed of light, wave/particle duality, natural constants, black holes, dark matter, and dark energy. Ekeberg’s incisive reading of the metaphysical underpinnings of scientific cosmology offers an innovative account of how we understand our place in the universe.


First published in 1974 as a companion volume to Darwin on Man by Howard E. Gruber, Paul Barrett’s transcriptions of Darwin’s M and N notebooks served to shed new light on the evolutionist’s methods and motivation.
According to Stephen Jay Gould in the New York Times Book Review, “Darwin kept [these notebooks] primarily in 1838, when he was 29 years old. In them, he recorded his early conviction of evolutionary continuity between humans and all other animals. . . . These notebooks display all the features of humanistic intellect that his detractors denied. We find erudition in his comments on Plato, Locke, Hume, Adam Smith, Whewell, Burke, Montaigne, Lessing and Spencer. . . . We appreciate an artistic bent in his delight with nature and her prophet Wordsworth. . . . We grasp the breadth of his bold attempt to clothe all human thought and behaviour in a new evolutionary garb. . . . Charles Darwin was reconstructing the world and he knew exactly what he was doing.”

Development of rural landscapes is converting once-vast expanses of open space into pockets of habitat where wildlife populations exist in isolation from other members of their species. The central concept of metapopulation dynamics -- that a constellation of partially isolated patches can yield overall stability to a system that is chaotic at the level of the individual patch -- offers an important new way of thinking about the conservation and management of populations dispersed among small habitat fragments. This approach is proving to be a rich resource for biologists hoping to arrest the current catastrophic loss of biodiversity.
An understanding of metapopulation theory and analysis is critical to the modern practice of wildlife conservation and management. This volume provides a comprehensive overview of the subject, addressing the needs of an applied professional audience for comprehensible information to integrate into their practices. Leading conservation biologists, ecologists, wildlife managers, and other experts consider the emergence and development of metapopulation theory and explore its applicability and usefulness to real-world conservation programs.
Introductory chapters provide background information on basic concepts such as models, genetics, landscape configuraton, and edges and corridors. Subsequent chapters present detailed methods of analyzing metapopulation structure. Case studies of an array of vertebrate species, including the Swedish pool frog, the northern spotted owl, Stephens' kangaroo rat, Florida scrub jay, Mediterranean monk seal, Steller sea lion, tule elk, and others, illustrate nuances of metapopulation theory analysis and its practical applications.
Contributors describe what metapopulation approaches bring to wildlife conservation and management, present models of how metapopulation thinking has been applied in specific situations, and suggest the analysis required in given cases. Metapopulations and Wildlife Conservation is essential reading for anyone working in the field of wildlife conservation and managment.


A richly illustrated, remarkably wide-ranging account of the culture and science surrounding meteorites, Golia’s book explores the ancient, lasting power of the meteorite to inspire and awe.

From the original publication:
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Source Regions 3. Secondary Processing 4. Irradiation Effects 5. Solar System Chronology 6. Chondrites and the Early Solar System 7. Elemental Composition of Chondrites 8. Magnetic Fields in the Early Solar System 9. Chondrules10. Primitive Material Surviving in chondrites11. Micrometeorites12. Inhomogencity of the Nebula13. Survival of Presolar Material in Meteorites14. Nucleosynthesis15. Nucleocosmochronology16. Summary


Hayes incorporates the iambic/trochaic opposition into a general theory of word stress assignment, intended to account for all languages in which stress is assigned on phonological as opposed to morphological principles. His theory addresses particularly problematic areas in metrical work, such as ternary stress and unusual weight distinctions, and he proposes new theoretical accounts of them. Attempting to take more seriously the claim of generative grammar to be an account of linguistic universals, Hayes proposes analyses for the stress patterns of over 150 languages.
Hayes compares his own innovative views with alternatives from the literature, allowing students to gain an overview of the field. Metrical Stress Theory should interest all who seek to understand the role of stress in language.

Upper-middle-class Americans are moving into larger homes in greater numbers, which leads Knox to explore the relationship between built form and material culture in contemporary society. He covers changes in home design, real estate, the work of developers, and the changing wishes of consumers. Knox shows that contemporary suburban landscapes are a product of consumer demand, combined with the logic of real estate development, mediated by design and policy professionals and institutions of governance. Suburban landscapes not only echo the fortunes of successive generations of inhabitants, Knox argues, they also reflect the country's changing core values.
Knox addresses key areas of concern and importance to today's urban planners and suburban residents including McMansions, traffic disasters, house design, homeowner's associations, exclusionary politics, and big box stores. Through the inclusion of examples and photos, Metroburbia, USA creates an accessible portrait of today's suburbs supported by data, anecdotes, and social theory. It is a broad interpretation of the American metropolitan form that looks carefully at the different influences that contribute to where and how we live today.


Mice in the Freezer, Owls on the Porch is in many ways a love story—about a quiet scientist and his flamboyant wife, but also about their passions for hunting, for wild lands, and for the grouse and raptor species that they were instrumental in saving from destruction.
From the papers and letters of Frederick and Frances Hamerstrom, the reminiscences of contemporaries, and her own long friendship with this extraordinary couple who were her neighbors, Helen Corneli draws an intimate picture of Fran and "Hammy" from childhood through the genesis and maturation of a romantic, creative, and scientific relationship. Following the Hamerstroms as they give up a life of sophisticated convention and comfort for the more "civilized" (as Aldo Leopold would have it) pleasures of living and conducting on-the-spot research into diminishing species, Corneli captures the spirit of the Hamerstroms, their profession, and the natural and human environments in which they worked. A nuanced account of the labors, adventures, and achievements that distinguished the Hamerstroms over the years—and that inspired a generation of naturalists—this book also provides a dramatic account of conservation history over the course of the twentieth century, particularly in Wisconsin during the eventful years from the 1920s through the 1970s.




Why the global health project to avert emerging microbes continually fails
In 1989, a group of U.S. government scientists met to discuss some surprising findings: new diseases were appearing around the world, and viruses that they thought long vanquished were resurfacing. Their appearance heralded a future perpetually threatened by unforeseeable biological risks, sparking a new concept of disease: the “emerging microbe.” With the Cold War nearing its end, American scientists and security experts turned to confront this new “enemy,” redirecting national security against its risky horizons. In order to be fought, emerging microbes first needed to be made perceptible; but how could something immaterial, unknowable, and ever mutating be coaxed into visibility, knowability, and operability?
Microbial Resolution charts the U.S.-led war on the emerging microbe to show how their uncertain futures were transformed into objects of global science and security. Moving beyond familiar accounts that link scientific knowledge production to optical practices of visualizing the invisible, Gloria Chan-Sook Kim develops a theory of “microbial resolution” to analyze the complex problematic that arises when dealing with these entities: what can be seen when there is nothing to see? Through a syncretic analysis of data mining, animal-tracking technologies, media networks, computer-modeled futures, and global ecologies and infrastructures, she shows how a visual impasse—the impossibility of seeing microbial futures—forms the basis for new modes of perceiving, knowing, and governing in the present.
Timely and thought provoking, Microbial Resolution opens up the rich paradoxes, irreconcilabilities, and failures inherent in this project and demonstrates how these tensions profoundly animate twenty-first-century epistemologies, aesthetics, affects, and ecologies.

For three centuries, concepts of the state have been animated by one of the most powerful metaphors in politics: the body politic, a claustrophobic and bounded image of sovereignty. Climate change, neoliberalism, mass migration, and other aspects of the late Anthropocene have increasingly revealed the limitations of this metaphor. Just as the human body is not whole and separate from other bodies—comprising microbes, bacteria, water, and radioactive isotopes—Stefanie R. Fishel argues that the body politic of the state exists in dense entanglement with other communities and forms of life.
Drawing on insights from continental philosophy, science and technology studies, and international relations theory, this path-breaking book critiques the concept of the body politic on the grounds of its very materiality. Fishel both redefines and extends the metaphor of the body politic and its role in understanding an increasingly posthuman, globalized world politics. By conceiving of bodies and states as lively vessels, living harmoniously with multiplicity and the biosphere, she argues that a radical shift in metaphors can challenge a politics based on fear to open new forms of global political practice and community.
Reframing the concept of the body politic to accommodate greater levels of complexity, Fishel suggests, will result in new configurations for the political and social organization necessary to build a world in which the planet’s inhabitants do not merely live but actively thrive.


Concentrating on Great Britain and the German lands—home to the period’s most significant developments in microscopy—The Microscope and the Eye examines debates about such subjects as the legitimacy of human trespassing on the microcosm and the nature of light. Schickore also explores the microscope’s role in investigations of the finer structure of the eye and the workings of nerve fibers and the microscopists’ reflections on vision, illusion, artifacts, and the merits of instruments. Fully considering the epistemological, metaphysical, and methodological implications of this centuries-old relationship, The Microscope and the Eye will be an important contribution to the history of the life sciences, vision studies, and scientific methodology.


The past decade has been characterized by remarkable advances in meteorological observation, computing techniques, and data-visualization technology. However, the benefit of these advances can only be fully realized with the introduction of a systematic, applied approach to meteorological education that allows well-established theoretical concepts to be applied to modernized observational and numerical datasets.




Insects that are the least bit social may gather in modest groups, like the dozen or so sawfly larvae feeding on a pine needle, or they may form huge masses, like a swarm of migratory locusts in Africa or a cloud of mayflies at the edge of a midwestern lake or river. Why these insects get together and what they get out of their associations are questions finely and fully considered in this learned and entertaining look at the group behavior and social lives of a wide array of bugs.
The groups that Gilbert Waldbauer discusses here are not as complex or tightly organized as the better-known societies of termites, wasps, ants, and bees. Some, like the mayflies, come together merely because they emerge from the water in the same place at the same time. But others, like swarms of locusts, are loosely organized, the individual insects congregating to migrate together for distances of hundreds of miles. And yet others form a simple cooperative society, such as the colony of tent caterpillars that weaves a silken tent to house the whole group.
Waldbauer tells us how individuals in these and other insect aggregations communicate (or don't), how they coordinate their efforts, how some congregate the better to mate, how some groups improve the temperature and humidity of their microenvironment, and how others safeguard themselves (or the future of their kind) by amassing in such vast numbers as to confound predators.
As engaging and authoritative as Waldbauer's previous books, Millions of Monarchs, Bunches of Beetles will enlighten and delight those who know their insects well and those who wish to know them better.

This exciting compendium brings together, for the first time, some of the foremost scholars of René Girard’s mimetic theory, with leading imitation researchers from the cognitive, developmental, and neuro sciences. These chapters explore some of the major discoveries and developments concerning the foundational, yet previously overlooked, role of imitation in human life, revealing the unique theoretical links that can now be made from the neural basis of social interaction to the structure and evolution of human culture and religion. Together, mimetic scholars and imitation researchers are on the cutting edge of some of the most important breakthroughs in understanding the distinctive human capacity for both incredible acts of empathy and compassion as well as mass antipathy and violence. As a result, this interdisciplinary volume promises to help shed light on some of the most pressing and complex questions of our contemporary world.

Offering up clinical studies and a complete reevaluation of classical psychiatry, Oughourlian explores the interaction among reason, emotions, and imitation and reveals that rivalry—the blind spot in contemporary neuroscientific understandings of imitation—is a misunderstood driving force behind mental illness. Oughourlian’s analyses shake the very foundations of psychiatry as we know it and open up new avenues for both theoretical research and clinical practice.


As part of his attempt to secure a place for women in scientific culture, the Cartesian François Poullain de la Barre asserted as long ago as 1673 that “the mind has no sex.” In this rich and comprehensive history of women’s contributions to the development of early modern science, Londa Schiebinger examines the shifting fortunes of male and female equality in the sphere of the intellect. Schiebinger counters the “great women” mode of history and calls attention to broader developments in scientific culture that have been obscured by time and changing circumstance. She also elucidates a larger issue: how gender structures knowledge and power.
It is often assumed that women were automatically excluded from participation in the scientific revolution of early modern Europe, but in fact powerful trends encouraged their involvement. Aristocratic women participated in the learned discourse of the Renaissance court and dominated the informal salons that proliferated in seventeenth-century Paris. In Germany, women of the artisan class pursued research in fields such as astronomy and entomology. These and other women fought to renegotiate gender boundaries within the newly established scientific academies in order to secure their place among the men of science. But for women the promises of the Enlightenment were not to be fulfilled. Scientific and social upheavals not only left women on the sidelines but also brought about what the author calls the “scientific revolution in views of sexual difference.”
While many aspects of the scientific revolution are well understood, what has not generally been recognized is that revolution came also from another quarter—the scientific understanding of biological sex and sexual temperament (what we today call gender). Illustrations of female skeletons of the ideal woman—with small skulls and large pelvises—portrayed female nature as a virtue in the private realm of hearth and home, but as a handicap in the world of science. At the same time, seventeenth- and eighteenth-century women witnessed the erosion of their own spheres of influence. Midwifery and medical cookery were gradually subsumed into the newly profess ionalized medical sciences. Scientia, the ancient female personification of science, lost ground to a newer image of the male researcher, efficient and solitary—a development that reflected a deeper intellectual shift. By the late eighteenth century, a self-reinforcing system had emerged that rendered invisible the inequalities women suffered. In reexamining the origins of modern science, Schiebinger unearths a forgotten heritage of women scientists and probes the cultural and historical forces that continue to shape the course of scientific scholarship and knowledge.

Understanding the chimpanzee mind is akin to opening a window onto human consciousness. Many of our complex cognitive processes have origins that can be seen in the way that chimpanzees think, learn, and behave. The Mind of the Chimpanzee brings together scores of prominent scientists from around the world to share the most recent research into what goes on inside the mind of our closest living relative.
Intertwining a range of topics—including imitation, tool use, face recognition, culture, cooperation, and reconciliation—with critical commentaries on conservation and welfare, the collection aims to understand how chimpanzees learn, think, and feel, so that researchers can not only gain insight into the origins of human cognition, but also crystallize collective efforts to protect wild chimpanzee populations and ensure appropriate care in captive settings. With a breadth of material on cognition and culture from the lab and the field, The Mind of the Chimpanzee is a first-rate synthesis of contemporary studies of these fascinating mammals that will appeal to all those interested in animal minds and what we can learn from them.
READERS
Browse our collection.
PUBLISHERS
See BiblioVault's publisher services.
STUDENT SERVICES
Files for college accessibility offices.
UChicago Accessibility Resources
home | accessibility | search | about | contact us
BiblioVault ® 2001 - 2024
The University of Chicago Press









